Protection of information from insiders pdf. How to protect yourself from insider? Systems based on context analyzers
Today, there are two main channels for leaking confidential information: devices connected to a computer (all kinds of removable drives, including flash drives, CD / DVD drives, etc., printers) and the Internet (e-mail, ICQ, social media etc.). And therefore, when a company is “ripening” to introduce a system of protection against them, it is advisable to approach this solution in a comprehensive manner. The problem is that different approaches are used to overlap different channels. In one case, the most effective way of protection will be control over the use of removable drives, and in the second, various options for content filtering, which allows you to block the transfer of confidential data to an external network. And so companies have to use two products to protect against insiders, which together form a comprehensive security system. Naturally, it is preferable to use the tools of one developer. In this case, the process of their implementation, administration, and training of employees is facilitated. An example is the products of SecurIT: Zlock and Zgate.
Zlock: leak protection through removable drives
The Zlock program has been on the market for a long time. And we already. In principle, there is no point in repeating. However, since the publication of the article, two new versions of Zlock have been released, which have a number of important features. It is worth talking about them, even if very briefly.
First of all, it is worth noting the possibility of assigning several policies to a computer, which are independently applied depending on whether the computer is connected to the corporate network directly, via VPN, or works offline. This allows, in particular, to automatically block USB ports and CD / DVD drives when the PC is disconnected from local network. Generally given function increases the security of information stored on laptops that employees can take out of the office for travel or to work at home.
The second new feature is giving company employees temporary access to locked devices or even groups of devices over the phone. The principle of its operation is to exchange generated by the program secret codes between the user and the person responsible for information security. It is noteworthy that permission to use can be issued not only permanent, but also temporary (for a certain time or until the end of the session). This tool can be considered as some relief in the security system, but it allows you to increase the responsiveness of the IT department to business requests.
The next important innovation in the new versions of Zlock is the control over the use of printers. After setting it up, the protection system will record all user requests to printing devices in a special log. But that's not all. Zlock has a shadow copy of all printed documents. They are written in PDF format and are a complete copy of the printed pages, regardless of which file was sent to the printer. This prevents the leakage of confidential information on paper sheets when an insider prints out the data in order to take it out of the office. Also in the protection system appeared shadow copying of information recorded on CD / DVD-disks.
An important innovation was the emergence of the server component Zlock Enterprise Management Server. It provides centralized storage and distribution of security policies and other program settings and greatly facilitates the administration of Zlock in large and distributed information systems. It is also impossible not to mention the emergence of its own authentication system, which, if necessary, allows you to abandon the use of domain and local Windows users.
In addition, in latest version Zlock has several not so noticeable, but also quite important functions: control of the integrity of the client module with the ability to block the user's login when intrusions are detected, advanced options for implementing a security system, support for the Oracle DBMS, etc.
Zgate: Internet Leak Protection
So Zgate. As we have already said, this product is a system for protecting against the leakage of confidential information via the Internet. Structurally Zgate consists of three parts. The main component is the server component, which performs all data processing operations. It can be installed both on a separate computer and on those already working in a corporate information system hosts - Internet gateway, domain controller, mail gateway, etc. This module, in turn, consists of three components: to control SMTP traffic, control internal mail of the Microsoft Exchange 2007/2010 server, and Zgate Web (it is responsible for control of HTTP, FTP and IM traffic).
The second part of the protection system is the logging server. It is used to collect information about events from one or more Zgate servers, process and store it. This module is especially useful in large and geographically distributed enterprise systems, as it provides centralized access to all data. The third part is the management console. It uses the standard console for SecurIT products, and therefore we will not dwell on it in detail. We only note that with the help of this module, you can manage the system not only locally, but also remotely.
Management Console
The Zgate system can operate in several modes. Moreover, their availability depends on the way the product is implemented. The first two modes involve working as a mail proxy server. To implement them, the system is installed between the corporate mail server and the "outside world" (or between the mail server and the sending server, if they are separated). In this case, Zgate can both filter traffic (detain infringing and questionable messages), and only log it (pass all messages, but keep them in the archive).
The second implementation method involves using the protection system in conjunction with Microsoft Exchange 2007 or 2010. To do this, you need to install Zgate directly on the corporate mail server. In this case, two modes are also available: filtering and logging. In addition, there is another implementation option. We are talking about logging messages in the mode of mirrored traffic. Naturally, in order to use it, it is necessary to ensure that the computer on which Zgate is installed receives this very mirrored traffic (usually this is done using network equipment).

Zgate operating mode selection
The Zgate Web component deserves a separate story. It is installed directly on the corporate Internet gateway. At the same time, this subsystem gets the ability to control HTTP, FTP, and IM traffic, that is, to process it in order to detect attempts to send confidential information through web mail interfaces and ICQ, publish it on forums, FTP servers, and social networks. etc. By the way, about "ICQ". The function of blocking IM-messengers is in many similar products. However, it is precisely “ICQ” that is not in them. Simply because it is in Russian-speaking countries that it has become most widespread.
The principle of operation of the Zgate Web component is quite simple. Each time information is sent to any of the controlled services, the system will generate a special message. It contains the information itself and some service data. It is sent to the main Zgate server and processed according to the given rules. Naturally, sending information in the service itself is not blocked. That is, Zgate Web only works in logging mode. With its help, it is impossible to prevent single data leaks, but on the other hand, you can quickly detect them and stop the activity of a free or unwitting attacker.

Configuring the Zgate Web Component
How information is processed in Zgate and the filtering order is determined by a policy that is developed by a security officer or other responsible employee. It is a series of conditions, each of which corresponds to a certain action. All incoming messages are "run" through them sequentially one after another. And if any of the conditions is met, then the action associated with it is launched.

Filtration system
In total, the system provides 8 types of conditions, as they say, "for all occasions." The first one is the attachment file type. With it, you can detect attempts to send objects of one format or another. It should be noted that the analysis is carried out not by extension, but by the internal structure of the file, and you can specify both specific types of objects and their groups (for example, all archives, video recordings, etc.). The second type of conditions is verification by an external application. As an application, it can act as a regular program launched from command line, as well as the script.

Conditions in the filtration system
But the next condition is worth dwelling on in more detail. We are talking about the content analysis of the transmitted information. First of all, it is necessary to note the "omnivorous" Zgate. The fact is that the program "understands" a large number of different formats. Therefore, it can analyze not only simple text, but also almost any attachment. Another feature of content analysis is its great potential. It can consist both in a simple search for an occurrence in the message text or any other field of a certain word, or in a full-fledged analysis, including taking into account grammatical word forms, stemming and transliteration. But that is not all. Special mention deserves the analysis system for patterns and regular expressions. With its help, you can easily detect the presence of data in a certain format in messages, for example, the series and numbers of a passport, phone number, contract number, bank account number, etc. This, among other things, allows you to strengthen the protection of personal data processed by the company.

Templates for identifying various sensitive information
The fourth type of conditions is the analysis of the addresses indicated in the letter. That is, search among them for certain strings. Fifth - analysis of encrypted files. When it is executed, the attributes of the message and/or nested objects are checked. The sixth type of conditions is to check various parameters of letters. The seventh is dictionary analysis. During it, the system detects the presence in the message of words from pre-created dictionaries. And, finally, the last, eighth type of condition is compound. It represents two or more other conditions combined with logical operators.
By the way, about the dictionaries mentioned by us in the description of the conditions, it is necessary to say separately. They are groups of words united by the same feature and are used in various filtering methods. It is most logical to create dictionaries that, with a high degree of probability, allow you to attribute the message to one category or another. Their content can be entered manually or imported from existing text files. There is another option for generating dictionaries - automatic. When using it, the administrator simply needs to specify the folder that contains the relevant documents. The program itself will analyze them, select the necessary words and arrange their weight characteristics. For high-quality compilation of dictionaries, it is necessary to indicate not only confidential files, but also objects that do not contain confidential information. In general, the process of automatic generation is most similar to learning anti-spam on promotional and regular emails. And this is not surprising, because both there and there similar technologies are used.

An example of a financial vocabulary
Speaking of dictionaries, one cannot fail to mention another technology for detecting confidential data implemented in Zgate. We are talking about digital prints. The essence of this method is as follows. The administrator can point the system to folders that contain sensitive data. The program will analyze all the documents in them and create "digital fingerprints" - data sets that allow you to determine the attempt to transfer not only the entire contents of the file, but also its individual parts. Please note that the system automatically monitors the status of the folders specified by it and independently creates "fingerprints" for all newly appeared objects in them.

Create a category with digital file fingerprints
Well, now it remains only to deal with the actions implemented in the protection system in question. In total, there are already 14 of them implemented in Zgate. However, the majority defines the actions that are performed with the message. These include, in particular, deleting without sending (that is, in fact, blocking the transmission of a letter), placing it in an archive, adding or deleting attachments, changing various fields, inserting text, etc. Among them, the quarantine of a letter is especially worth noting. This action allows you to "postpone" the message for manual verification by the security officer, who will decide on its future fate. Also very interesting is the action that allows you to block the IM connection. It can be used to instantly block the channel through which a message with confidential information was transmitted.
Two actions stand out somewhat - Bayesian processing and fingerprint processing. Both are designed to check messages for sensitive information. Only the first uses dictionaries and statistical analysis, while the second uses digital fingerprints. These actions can be performed when a certain condition is met, for example, if the recipient's address is not in the corporate domain. In addition, they (however, like any others) can be set for unconditional application to all outgoing messages. In this case, the system will analyze letters and classify them into certain categories (if, of course, this is possible). But for these categories, it is already possible to make conditions with the implementation of certain actions.

Actions in the Zgate system
Well, at the end of our today's conversation about Zgate, we can sum up a little. This system protection is based primarily on the content analysis of messages. This approach is the most common for protection against leakage of confidential information via the Internet. Naturally, content analysis does not provide a 100% degree of protection and is rather probabilistic. However, its use prevents most cases of unauthorized transfer of secret data. Should companies use it or not? Everyone should decide this for himself, evaluating the costs of implementation and possible problems in case of information leakage. It is worth noting that Zgate does an excellent job of "catching" regular expressions, which makes it a very effective means of protecting personal data that is being processed by the company.
"Consultant", 2011, N 9
"He who owns the information owns the world" - this famous aphorism of Winston Churchill is more relevant than ever in modern society. Knowledge, ideas and technology come to the fore, and market leadership depends on how well a company can manage its intellectual capital.
Under these conditions, the information security of the organization is of particular importance.
Any leak of information to competitors or disclosure of information about internal processes instantly affects the positions that the company occupies in the market.
The information security system should provide protection against a variety of threats: technical, organizational and those caused by the human factor.
As practice shows, insiders are the main channel of information leakage.
Enemy in the rear
It is customary to call an insider an employee of a company who harms the company by disclosing confidential information.
However, if we consider the three main conditions, the provision of which is the goal of information security - confidentiality, integrity, availability - this definition can be expanded.
An insider can be an employee who has legitimate official access to the company's confidential information, which becomes the cause of disclosure, distortion, damage or inaccessibility of information.
This generalization is valid, because in today's world, the violation of the integrity and availability of information often entails much more serious consequences for business than the disclosure of confidential information.
For many businesses, shutting down business processes, even for a short time, threatens to tangible financial losses, and a disruption of functioning within a few days can strike so hard that the consequences can be fatal.
Various organizations that study business risks regularly publish their research results. According to them, insider information has consistently ranked first in the list of causes of information security breaches for many years.
Due to the steady growth in the total number of incidents, it can be concluded that the urgency of the problem is increasing all the time.
Threat model
In order to build a reliable layered information security system that will help to effectively deal with the problem, it is necessary first of all to create a threat model.
It is necessary to understand who insiders are and what drives them, why they perform certain actions.
There are different approaches to creating such models, but for practical purposes, you can use the following classification, which includes all the main types of insiders.
Internal "hacker"
Such an employee, as a rule, has an engineering qualification above the average level, understands the organization of enterprise resources, the architecture of computer systems and networks.
He performs hacking actions out of curiosity, sports interest, exploring the boundaries of his own capabilities.
Usually he is aware of the possible harm from his actions, so he rarely brings tangible damage.
The degree of danger is medium, since his actions can cause a temporary stop of some processes taking place in the company. Identification of activity is possible primarily by technical means.
Irresponsible and low-skilled employee
Can have different skills and work in any department of the enterprise.
It is dangerous because it does not tend to think about the consequences of its actions, it can work with the company's information resources "by trial and error", unintentionally destroy and distort information.
Usually he does not remember the sequence of his actions, and when he finds negative consequences, he can simply keep silent about them.
May reveal trade secrets in a face-to-face conversation with a friend, or even in online forums and social media.
The degree of danger is very high, especially considering that this type of intruder is more common than others. The consequences of his activities can be much more serious than those of a conscious attacker.
In order to prevent the consequences of his actions, it is necessary to take a whole range of different measures, both technical (authorization, mandatory division of work sessions into accounts) and organizational (constant management control over the process and the result of work).
Psychologically unstable person
Just like a representative of the previous type, he can work in any position and have very different qualifications. Dangerous due to a tendency to act poorly motivated in conditions of psychological discomfort: in extreme situations, psychological pressure from other employees, or simply strong irritation.
In an affective state, it can give out confidential information, damage data, disrupt the usual course of work of other people.
The degree of danger is medium, but this type of intruder is not so common.
To prevent the negative consequences of his actions, it is most effective to use administrative measures - to identify such people at the interview stage, to differentiate access to information and maintain a comfortable psychological climate in the team.
Offended, offended employee
The widest group of potential violators of the information security regime.
Theoretically, the vast majority of employees are capable of committing acts unfriendly to the company.
This can happen if the management shows disrespect for the personality of the employee or his professional qualities, and when this affects the level of remuneration.
Potentially, this type of insider poses a very high danger - both leaks and damage to information are possible, and the harm from them will be guaranteed to be noticeable to the business, since the employee inflicts it deliberately and knows all the vulnerabilities well.
Both administrative and technical measures are needed to detect activity.
Dishonest employee
An employee who seeks to supplement his personal wealth from the assets of the company he works for. Among the things assigned may be various carriers of confidential information ( hard drives, flash drives, corporate laptops).
In this case, there is a risk that information will get to people for whom it was not intended, with subsequent publication or transfer to competitors.
The danger is medium, but this type is not uncommon.
First of all, administrative measures are needed to identify them.
Competitor representative
As a rule, he is highly qualified, holds positions that provide ample opportunities for obtaining information, including confidential information. This is either an active employee recruited by competitors (more often), or an insider specially introduced into the company.
The degree of danger is very high, since the harm is done deliberately and with a deep understanding of the value of information, as well as the vulnerabilities of the company.
Both administrative and technical measures are needed to identify activities.
What are we stealing?
Understanding the insider problem is impossible without considering the nature of the stolen information.
According to statistics, personal data of clients, as well as information about client companies and partners, are the most sought after, they are stolen in more than half of cases. Further details of transactions, conditions of contracts and deliveries follow. Financial reports are also of great interest.
When forming a set of protective measures, the question inevitably arises for each company: what specific information requires special protective measures, and what does not need them?
Of course, the basis for such decisions is the data obtained as a result of risk analysis. However, often an enterprise has limited financial resources that can be spent on an information security system, and they may not be enough to minimize all risks.
Two approaches
Unfortunately, there is no ready answer to the question: "What to protect in the first place."
This problem can be approached from two sides.
Risk is a complex indicator that takes into account both the likelihood of a particular threat and the possible damage from it. Accordingly, when prioritizing security, you can focus on one of these indicators. This means that, first of all, the information that is easiest to steal (for example, if a large number of employees have access to it) is protected, and that information, theft or blocking of which will lead to the most serious consequences.
An important aspect of the insider problem is the channel of information transmission. The more physical opportunities for unauthorized transfer of information outside the company, the higher the likelihood that this will happen.
Transmission mechanisms
Transmission mechanisms can be classified as follows:
- oral transmission (personal conversation);
- technical data transmission channels (telephone communication, facsimile communication, e-mail, messaging systems, various social Internet services, etc.);
- portable media and mobile devices (mobile phones, external hard drives, laptops, flash drives, etc.).
According to research, in our time, the most frequent channels for transmitting confidential data are (in descending order): e-mail, mobile devices (including laptops), social networks and other Internet services (such as instant messaging systems) and so on.
To control technical channels, various means can be used, which are now in a wide range on the security market.
For example, content filtering systems (dynamic blocking systems), means of restricting access to information media (CD, DVD, Bluetooth).
Administrative measures are also applied: filtering Internet traffic, blocking physical ports of workstations, ensuring administrative regime and physical protection.
When choosing technical means of protecting confidential information, it is necessary to apply a systematic approach. Only in this way it is possible to achieve the greatest efficiency from their implementation.
You also need to understand that the challenges facing each company are unique, and it is often simply impossible to use solutions used by other organizations.
The fight against insider information should not be carried out on its own; it is an important component of the overall business process aimed at ensuring the information security regime.
It should be carried out by professionals and include a full cycle of activities: the development of an information security policy, the definition of the scope, risk analysis, the selection of countermeasures and their implementation, as well as the audit of the information security system.
If an enterprise does not provide an information security regime for the entire complex, then the risks of financial losses from leaks and information corruption increase dramatically.
Risk minimization
Examination
- Thorough screening of applicants applying for any position in the company. It is recommended to collect as much information about the candidate as possible, including the content of his pages on social networks. It can also help to apply for a reference to a previous job.
- Candidates for positions of IT engineers should be subjected to especially thorough scrutiny. Practice shows that more than half of all insiders are system administrators and programmers.
- When hiring, at least a minimum psychological test of candidates should be carried out. It will help identify applicants with an unstable psyche.
Access right
- The system of sharing access to corporate resources. The enterprise should create regulatory documentation that ranks information according to the level of confidentiality and clearly defines the rights of access to it. Access to any resources must be personalized.
- Access rights to resources should be allocated according to the principle of "minimum sufficiency". Access to maintenance of technical facilities, even with administrator rights, does not always have to be accompanied by access to view the information itself.
- As far as possible, deep monitoring of user actions, with mandatory authorization and recording of information about the operations performed in the log. The more carefully the logs (logs) are kept, the more the management controls the situation in the company. The same applies to the actions of an employee when using service access to the Internet.
Communication standard
- Within the organization, its own standard of communication should be adopted, which would exclude all forms of incorrect behavior of employees towards each other (aggression, violence, excessive familiarity). First of all, this applies to the relationship "leader - subordinate".
Under no circumstances should an employee feel that he is being treated unfairly, that he is not valued enough, that he is being overly exploited, that he is being deceived.
Compliance with this simple rule will allow you to avoid the vast majority of situations that provoke employees to insider knowledge.
Confidentiality
A non-disclosure agreement should not be a mere formality. It must be signed by all employees who have access to important information resources of the company.
In addition, even at the interview stage, potential employees need to be explained how the company controls information security.
Funds control
Represents the control of technical means used by the employee for work purposes.
For example, the use of a personal laptop is undesirable, since when an employee leaves, most likely it will not be possible to find out what information is stored on it.
For the same reason, the use of boxes is undesirable. Email on external resources.
internal order
The company must comply with the internal regulations.
It is necessary to have information about the time spent by employees at the workplace.
Also, control over the movement of material assets should be ensured.
Compliance with all these rules will reduce the risk of damage or leakage of information through insider information, which means it will help prevent significant financial or reputational losses.
Managing partner
Hosting Community group of companies
The rapid development of information technology and modern means of communication has greatly complicated the control over data flows. It is simply impossible to imagine the normal operation of a company without e-mail, Internet pagers, mobile devices and other means of prompt transmission of information. Accounting documents, financial reports, databases, contracts with clients, development plans and other confidential information are stored and processed in in electronic format, which means that they can be partially or completely copied and transferred to attackers.
Risk identification
According to the analytical center InfoWatch, in 2007 more than 500 insider incidents were recorded in the world, the total damage from which amounted to about $58 billion, which is 30% more than in 2006. It is clear that there can be many times more undetected cases of information leakage. If we talk about the situation in Russia, then the scale of the problem is evidenced, for example, by the number of illegal software with all kinds of databases at affordable prices.
Identification of information risks can begin with clarifying the question of what kind of data and through what channels are most often leaked from Russian companies. During the study "Insider Threats 2008" conducted by the analytical center Perimetrix, representatives of more than 470 domestic enterprises were interviewed. According to respondents, personal data is most often stolen from companies, including customer information (57%), as well as details of specific transactions (47%) and financial statements (38%), followed by intellectual property (25%) and business plans. (19%) (Fig. 1)

Source: Perimetrix Insider Threats 2008 study
In the same study, high-capacity mobile storage devices (such as those based on flash memory or magnetic platters) were recognized as the most common channel for leaking confidential data (Figure 2). Another study of internal information security incidents conducted by the InfoWatch analytical center also showed that in 2007 the largest number of information leaks occurred through mobile devices (laptops, PDAs, USB flash drives, CDs and DVDs, etc.).
The second most popular method of transferring secret information was corporate e-mail, access to which is now available to almost every office worker. The fact is that not all companies filter email traffic for confidential data, and content filtering methods may be ineffective. Approximately two times less often than work e-mail, insiders use web mail (mail.ru, yandex.ru, etc.) and Internet pagers. This may be due to Internet access restrictions that are in place in many organizations.

Source: Perimetrix study Insider Threats 2008
However, mercenary insiders are just one of the categories of unscrupulous employees who pose a threat to the company's internal information security. As studies show, significantly more leaks occur through the fault of careless employees who neglect elementary information security tools (CCleaner) or violate job descriptions for working with confidential data. Examples include the loss of USB drives or laptops with unencrypted data, or situations where employees, without their own selfish intent, turn out to be suppliers of valuable information to intruders who mislead them.
Thus, the results of the research allow us to identify several problem areas that are associated with the main threats to internal information security for most Russian companies:
- lack of control over copying confidential documents to removable media or external devices connected through various ports and wireless networks;
- lack of logging of transactions with confidential documents stored in electronic form;
- lack of control over the printing of confidential documents;
- lack of control over confidential documents taken outside the company on employee laptops.
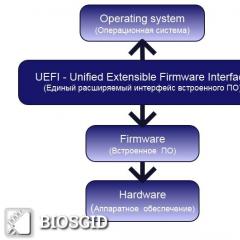
It is clear that it is practically impossible to minimize the risks in these areas with the help of information security systems that are used today in most Russian companies. Antiviruses, firewalls, access control and intrusion detection / prevention systems (IDS / IPS), which form the basis of the information security of many domestic enterprises, are mainly focused on protection against external threats and are of little use for dealing with insiders.
To prevent leaks of confidential information related to the actions of the employees themselves, comprehensive measures are needed to build an internal information security management system and introduce a trade secret regime.
Ensuring internal information security
The introduction of an internal information security system in an enterprise is a long and very costly process, so it is recommended to divide it into several sequentially implemented stages. First of all, it is necessary to classify all inside information with division into categories according to the level of confidentiality. The data that employees work with can be divided into public (without access restrictions), sensitive ( limited access), personal and confidential (special permission for use).
At the next stage, it is necessary to determine where information of various access categories is stored and how it is processed, as well as who is responsible for its safety. For each category of information, it will be necessary to prescribe procedures for handling it: how to copy, store, transfer and destroy. For this purpose, an inventory of resources used in working with information is carried out. Some experts propose to allocate information, software and physical resources during such an audit. Information resources containing confidential information may include files, databases, manual documentation, and the like. Software resources that process confidential information include application programs, DBMS (MS SQL, Oracle), document management tools, as well as mail systems and proxy servers through which information passes and is cached. Physical resources in which confidential information is processed include servers, workstations, removable media, laptops, communication equipment, etc. An example of an inventory of information resources is presented in Table. one.
Table 1. An example of an inventory of information resources
Type of information |
Location |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Production |
Production plans, intellectual property, technology descriptions, in-house developments |
File servers, DBMS |
Confidential |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
infrastructure |
IT infrastructure cards, IT systems, logins |
Locally |
sensitive |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Financial |
Accounting information, financial plans, reports, balance sheets |
Base 1C or other environment for the financial department |
Confidential |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Personnel |
Personnel cards |
Locally, file server |
sensitive |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Files and documents for internal sharing |
Personal |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Intracorporate |
Meeting reports, orders, directives, articles |
File Server |
Public |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Entertaining |
Photos, videos, movies, audiobooks |
Extended folders or dedicated file server |
According to various analytical companies, information leakage very often occurs not due to its theft from the outside, but due to the transfer of confidential information by their own employees to representatives of competing organizations. Today, there are many different devices to which any documents stored on the organization's local network can be copied. According to various analytical companies, information leakage very often occurs not due to its theft from the outside, but due to the transfer of confidential information by their own employees to representatives of competing organizations. Today, there are many different devices to which any documents stored on the organization's local network can be copied. And it's not just external USB drives or CD/DVD drives. You can also copy information to mp3 players, Cell Phones, which may or may not connect directly to a computer, to external equipment that can connect to a local network via Wi-Fi and in other ways. In addition, this is sending by e-mail, by means of instant messaging programs, through forums, blogs, and chats. There are many options, is it possible to protect yourself from them? For protection of data from insiders apply various methods, which include the use of special programs designed to control the use peripherals. In this article, we will consider several programs, both foreign manufacturers and domestic ones, and try to determine where and when they should be applied. The program is designed for access restrictions to various peripheral devices, with the ability to create "white" lists, monitor user activity, shadow copy files copied to or from controlled devices. It is possible to install tracking drivers both centrally and locally. The application can be installed both centrally and locally if access to the protected computer via the network is limited or impossible. A single distribution kit includes several modules: server, installed on the server of the office local network allows / prohibits certain actions, saves information to the database; client, implemented as a tracking driver; administrator and database, which is used as SQLite. Tracking drivers provide control various ports, including USB, CIM, LPT, WiFi, IR and others. Depending on the port type, you can deny access completely, allow reading, or allow full access to the device. There is no distribution of access over time. It was also noticed that when allowing read-only access to devices such as USB flash drives, the ability to edit ordinary text files on these devices with the ability to save them on the same media remains. Shows USB devices connected to computers and keeps a log of user actions with external storage drives. Information about the connection/disconnection time of devices and about which files and when were read or written is stored in the database. Implemented shadow copying of files that were read from or written to USB devices. There is no shadow copying of files sent for printing or other devices, they are only logged. There is a concept of a "white list", which includes USB devices, access to which must always be open on all computers (for example, USB keys). This list is the same for all computers; there are no individual lists for individual users.
It has the ability to use a centralized installation of client parts using group policy Active Directory. At the same time, you can install them locally and through the program administrator panel. Differentiation of access rights is carried out on the basis of access control policies, however, it is possible to create several policies that can be applied individually for different computers. In addition to the access control function, it allows logging the use of devices on the local computer. The program supports the shadow copy function - the ability to save an exact copy of files copied by the user to external storage devices. Exact copies of all files are stored in a special storage and can later be analyzed using the built-in analysis system. Shadow copying can be set for individual users and user groups. When the "keep only log" function is enabled, when copying files, only information about them will be saved (without saving an exact copy of the file). The program does not have the concept of a "white list" of devices. Instead, you can specify removable media in the general policy and allow access to it from any computer. Note that there is no way to apply the same settings to individual CD/DVDs.
The program provides three typical settings for access rights - for servers, workstations and laptops. In addition to device blocking, the program has the possibility access blocking files depending on their type. For example, you can allow read access to document files, but deny access to executable files. It is also possible to block access to devices not only by their type, but also by the physical port to which external devices are connected. One more setting access rights conducted by unique device identifiers. The application administrator can maintain two types of device lists - those that are allowed by default ("white list") and those that are denied access ("black list"). An IT specialist can give temporary permissions to access devices or groups of devices on a single computer (implemented by generating a special code that can be transmitted to the user even if his computer is disconnected from the network and the application agent is unable to connect to the server ). The program implements support for a new encryption function used in Windows system 7 called BitLocker To Go. This feature is used to protect and encrypt data on removable devices. GFI EndPointSecurity can recognize these devices and provide access to the files stored on them depending on their types. Provides the administrator with a powerful reporting system. The statistics subsystem (GFI EndPointSecurity ReportPack) shows (in textual and graphical form) a daily summary of device usage both for selected computers and for all computers in general. You can also get statistical data on user activity by day, week, month, broken down by applications used, devices, file access paths.
The program provides control not only devices running under Windows control Mobile, but also devices running the iPhone OS and Palm OS operating systems. At the same time, shadow copying of all overwritten files and data is also provided, regardless of which port these devices are connected to the monitored network. Shadow copying can be configured not only by device, but also by file type, and the type will be determined not on the basis of extensions, but on the basis of their content. You can set read-only access for removable media, including tape drives. As an additional option - protection of media from accidental or deliberate formatting. You can also keep a record of all user actions with both devices and files (not only copying or reading, but also deleting, renaming, and so on). Streaming compression can be used to reduce network load when transferring data received from agents and shadow copy files. Shadow copy data in large networks can be stored on multiple servers. The program automatically selects the optimal server, taking into account network bandwidth and server load. Many organizations use disks protected by special encryption programs - ViPNet SafeDisk, PGP Whole Disk Encryption, DriveCrypt and TrueCrypt to protect data. For such disks, the program can set special "encryption policies", which allows you to allow only encrypted data to be written to removable devices. Work is also supported with Lexar JumpDrive SAFE S3000 and Lexar SAFE PSD flash drives that support hardware data encryption. In the next version, work with the data encryption tool built into Windows 7 on removable media BitLocker To Go will also be supported.
Shadow copying is designed not only to save copies of files, but also to analyze the moved information. can perform full-text search on the contents of files, automatically recognizing and indexing documents in various formats. Already announced new version a program that, in addition to a full-fledged search, will also implement content filtering of files copied to removable storage devices of any type, as well as control of the content of data objects transmitted from a computer through network communication channels, including email applications, interactive web services, social networks, forums and conferences, the most popular Instant Messengers, FTP file exchanges, and Telnet sessions Unique in the new version is the technology of text data filtering in the network and local document printing channel for jobs in PCL and PostScript formats, which allows blocking or allowing printing of documents depending on their information content. conclusions
The first two of the programs discussed can be used to information security from theft, but their possibilities are limited. They "close" standard external devices to varying degrees, but their capabilities are limited - both in terms of settings and in terms of analyzing user work. These programs can be recommended "for testing", to understand the very process of protection. For large organizations that use a variety of peripheral equipment and require analysis of user activity, the above programs will be clearly insufficient. For them, it is better to pay attention to programs - and. These are professional solutions that can be used in companies with both small and large number of computers. Both programs provide control of various peripheral devices and ports, have powerful analysis and reporting systems. But there are significant differences between them, so the company's program GFI in this case can be taken as the base. can control not only devices and work with data, but also the use of software. This feature "pulls" it from the "Device Control" niche to the "Content-Aware Endpoint DLP" segment. New, announced capabilities allow it to sharply break away from its competitors due to the emergence of the ability to analyze content at the time the user performs various actions with data, including streaming, as well as by controlling a number of network communication context parameters, including email addresses, IP addresses, user IDs and network application resources, etc. it is possible at partners "1Soft". Mikhail Abramzon All rights reserved. For information about using this article, please contact site administrators Protection of information from insiders using software tools Alexander Antipov I hope that the article itself, and especially its discussion, will help identify various nuances of using software tools and become a starting point in developing a solution to the described problem for information security specialists. nahna The marketing department of Infowatch has been convincing all interested parties - IT specialists, as well as the most advanced IT managers for a long time, that most of the damage from a violation of the company's information security falls on insiders - employees who disclose trade secrets. The goal is clear - it is necessary to create demand for the manufactured product. Yes, and the arguments look quite solid and convincing. Formulation of the problemBuild a system for protecting information from theft by personnel in a LAN based on Windows 2000/2003 Active Directory. User workstations running Windows XP. Enterprise management and accounting based on 1C products.Secret information is stored in three ways:
What's on the marketI divided the systems under consideration into three classes:
Systems based on context analyzersPrinciple of operation:The transmitted information is searched for keywords, based on the results of the search, a decision is made on the need to block the transmission. In my opinion, InfoWatch Traffic Monitor (www.infowatch.ru) has the maximum potential among the listed products. The well-proven Kaspersky Antispam engine, which most fully takes into account the peculiarities of the Russian language, is taken as a basis. Unlike other products, InfoWatch Traffic Monitor, when analyzing, takes into account not only the presence of certain lines in the data being checked, but also the predefined weight of each line. Thus, when making a final decision, not only the occurrence of certain words is taken into account, but also the combinations in which they occur, which allows increasing the flexibility of the analyzer. Other features are standard for such products - analysis of archives, MS Office documents, the ability to block the transfer of files of unknown format or password-protected archives. Disadvantages of the considered systems based on contextual analysis:
contextual analysis is only suitable for creating traffic archives and counteracting accidental information leakage, and does not solve the task. Systems based on static blocking of devicesPrinciple of operation:users are assigned access rights to controlled devices, similar to file access rights. In principle, almost the same effect can be achieved using standard Windows mechanisms. Zlock (www.securit.ru) - the product appeared relatively recently, so it has minimal functionality (I don’t think it’s frills), and it doesn’t differ in debugging, for example, the control console sometimes crashes when trying to save settings. DeviceLock (www.smartline.ru) is a more interesting product, it has been on the market for a long time, so it works much more stable and has more diverse functionality. For example, it allows shadow copying of transmitted information, which can help in the investigation of an incident, but not in its prevention. In addition, such an investigation is likely to be carried out when the leak becomes known, i.e. a considerable period of time after it occurs. InfoWatch Net Monitor (www.infowatch.ru) consists of modules - DeviceMonitor (analogous to Zlock), FileMonitor, OfficeMonitor, AdobeMonitor and PrintMonitor. DeviceMonitor is an analogue of Zlock, standard functionality, without raisins. FileMonitor - control of access to files. OfficeMonitor and AdobeMonitor allow you to control how files are handled in their respective applications. It is currently quite difficult to come up with a useful, and not a toy, application for FileMonitor, OfficeMonitor and AdobeMonitor, but in future versions it should be possible to contextually analyze the data being processed. Perhaps then these modules will reveal their potential. Although it is worth noting that the task of contextual analysis of file operations is not trivial, especially if the content filtering base is the same as in Traffic Monitor, i.e. network. Separately, it is necessary to say about protecting the agent from a user with local administrator rights. DeviceLock has such protection, which is a definite plus. It is based on intercepting system calls for working with the registry, file system and process management. Another plus is that protection works in safe-mode as well. But there is also a minus - to disable protection, it is enough to restore the Service Descriptor Table, which can be done by loading a simple driver. Disadvantages of the considered systems based on static blocking of devices:
it is not advisable to introduce such systems, because they don't solve the problem. Systems based on dynamic blocking of devicesPrinciple of operation:access to transmission channels is blocked depending on the user's access level and the degree of secrecy of the information being worked with. To implement this principle, these products use the mechanism of authoritative access control. This mechanism is not very common, so I will dwell on it in more detail. Authoritative (forced) access control, in contrast to descriptive (implemented in the security system of Windows NT and higher), consists in the fact that the owner of a resource (for example, a file) cannot weaken the requirements for access to this resource, but can only strengthen them within your level. The requirements can be relaxed only by a user endowed with special powers - an officer or information security administrator. The main goal of developing products such as Guard, Accord, SecretNet, DallasLock and some others was the possibility of certification of information systems in which these products will be installed, for compliance with the requirements of the State Technical Commission (now FSTEC). Such certification is obligatory for information systems in which the state is processed. secret, which basically ensured the demand for products from state-owned enterprises. Therefore, the set of functions implemented in these products was determined by the requirements of the relevant documents. Which, in turn, led to the fact that most of the functionality implemented in the products either duplicates the standard Windows functionality (clearing objects after deletion, clearing RAM), or uses it implicitly (describing access control). And the developers of DallasLock went even further, implementing the mandatory access control of their system, through the Windows description control mechanism. The practical use of such products is extremely inconvenient, for example, DallasLock requires repartitioning for installation. hard drive, which also needs to be performed using third-party software. Very often, after certification, these systems were removed or turned off. SecrecyKeeper (www.secrecykeeper.com) is another product that implements an authoritative access control mechanism. According to the developers, SecrecyKeeper was developed specifically to solve a specific problem - preventing information theft in a commercial organization. Therefore, again, according to the developers, during the development, special attention was paid to simplicity and ease of use, both for system administrators and for ordinary users. How successful this is is for the consumer to judge, i.e. US. In addition, SecrecyKeeper implements a number of mechanisms that are not available in the other systems mentioned - for example, the ability to set the security level for resources with remote access and the agent protection mechanism. public - not secret information, there are no restrictions when working with it; secret - secret information, when working with it, restrictions are introduced depending on the User Permission Levels; top secret - top secret information, when working with it, restrictions are introduced depending on the User Permission Levels. The Security Level of Information can be set for a file, network drive and the port of the computer on which some service is running. User Permission Levels allow you to determine how a user can move information, depending on its Privacy Level. The following User Access Levels exist: User Access Level - limits the maximum Security Level of Information to which an employee can access; Level of Access to the Network - limits the maximum Level of Secrecy of Information that an employee can transmit over the network; Removable Media Access Level - limits the maximum Confidentiality Level of Information that an employee can copy to external media. Printer Security Level - limits the maximum Security Level of Information that an employee can print. Computer Security Level - determines the maximum Security Level of Information that can be stored and processed on a computer. Access to information with a level of secrecy public, can be carried out by an employee with any level of access. Such information can be transmitted over the network without restrictions and copied to external media. The history of working with information with the public secret level is not tracked. Access to information with a secret level of secret can only be obtained by employees whose clearance level is secret or higher. Only employees whose access level to the network is secret or higher can transfer such information to the network. Copying such information to external media can only be done by employees whose removable media access level is secret or higher. Printing such information can only be done by employees whose printer access level is secret or higher. The history of working with information that has a secret level of secret, i.e. attempts to access it, attempts to transfer it over the network, attempts to copy it to external media or print it are logged. Access to information with a top secret level can only be obtained by employees whose clearance level is equal to top secret. Only employees whose access level to the network is equal to the top secret can transfer such information to the network. Copying such information to external media can only be done by employees whose removable media access level is equal to the top secret. Only employees with a printer access level equal to top secret can print such information. The history of working with information that has a top secret level of secrecy, i.e. attempts to access it, attempts to transfer it over the network, attempts to copy it to external media or print it are logged. Example: Let an employee have a Security Level of top secret, a Network Security Level of secret, a Removable Media Security Level of public, and a Printer Security Level of top secret; in this case, the employee can access a document with any level of secrecy, the employee can transfer information with a secrecy level no higher than secret to the network, copy, for example, to floppy disks, the employee can only information with the public secrecy level, and the employee can print any information on a printer . To control the dissemination of information to the enterprise, each computer assigned to an employee is assigned a Computer Security Level. This level limits the maximum Information Security Level that any employee can access from this computer, regardless of the employee's clearance levels. That. if an employee has a Permission Level equal to top secret, and the computer on which he is currently working has a Security Level equal to public, then the employee will not be able to access information with a secret level higher than public from this workstation. Armed with theory, let's try to use SecrecyKeeper to solve the problem. It is possible to describe in a simplified way the information processed in the information system of the abstract enterprise under consideration (see the statement of the problem), using the following table: The employees of the enterprise and the area of their job interests are described using the second table: Let the following servers be used in the enterprise: I note that standard features are used to organize standard access control. operating system and application software, i.e. in order to prevent, for example, a manager from accessing the personal data of employees, no additional security systems need to be introduced. We are talking about counteracting the dissemination of information to which the employee has legal access. Let's proceed to the direct configuration of SecrecyKeeper. Step 1. Install agents on all PCs except servers - this immediately prevents them from getting information for which the Security Level is set higher than public. Step 2. Assign clearance levels to employees according to the following table:
Step 3. Assign Computer Security Levels as follows: Step 4. Configure Information Privacy Levels on Servers: Step 5. Set up Privacy Levels on Employees' PCs for Local Files. This is the most time-consuming part, since it is necessary to clearly understand which of the employees works with what information and how critical this information is. If an information security audit has been conducted in an organization, its results can greatly facilitate the task. Step 6. If necessary, SecrecyKeeper allows you to limit the list of programs allowed to run by users. This mechanism is implemented independently of the Windows Software Restriction Policy and can be used if, for example, it is necessary to impose restrictions on users with administrator rights. Thus, with the help of SecrecyKeeper, it is possible to significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized distribution of secret information - both leakage and theft. Disadvantages: General conclusion: Company is a unique service for buyers, developers, dealers and affiliate partners. In addition, this is one of the best online software stores in Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, which offers customers a wide range of products, many payment methods, prompt (often instant) order processing, tracking the order fulfillment process in the personal section. Share with friends or save for yourself:
|

 provides configuration of access to various external devices, but does not select printers connected to these ports from the general list of USB devices. At the same time, it distinguishes between removable media and can set different types of access for them. Removable media is automatically added to the device database (the program will add to the database all USB drives that have ever been connected to a particular computer), which allows you to apply the access rights assigned to them for any computers protected by the program.
provides configuration of access to various external devices, but does not select printers connected to these ports from the general list of USB devices. At the same time, it distinguishes between removable media and can set different types of access for them. Removable media is automatically added to the device database (the program will add to the database all USB drives that have ever been connected to a particular computer), which allows you to apply the access rights assigned to them for any computers protected by the program. Company program GFI significantly surpasses both in its capabilities and - in it, for example, there are much more controlled devices than previous programs (iPod media players, Creative Zen, mobile phones, digital cameras, archiving tools on magnetic tapes and Zip-disks, Web cameras, scanners).
Company program GFI significantly surpasses both in its capabilities and - in it, for example, there are much more controlled devices than previous programs (iPod media players, Creative Zen, mobile phones, digital cameras, archiving tools on magnetic tapes and Zip-disks, Web cameras, scanners). One of the most common programs for protecting information from insiders in Russia today. is published in Russia under the brand name "1C: Distribution"
One of the most common programs for protecting information from insiders in Russia today. is published in Russia under the brand name "1C: Distribution"