Kali Linux Guide: Penetration Testing. The Best Distributions for Penetration Testing Why Hackers Don't Use Windows
Kali linux is a tool for auditing information systems. Dozens of programs are built into this distribution kit, with the help of which you can detect vulnerabilities in various services and services.
I hope you remember that the use of this distribution for malicious purposes is punishable by the criminal code of the Russian Federation.

Since we are not looking for easy ways, we will install it ourselves, download the kali-linux-2.0-amd64.iso image, 3.09 GB in size.
And so, we create a virtual machine in WMvare or virtualbox and start the installation.
The first thing we see is the choice of installation options. These are several options for live installation, such as:
- failsafe (safe)
- persistence - live version with saving changes to disk,
- encrypted persistence - with encryption
- forensic mode, “judicial mode”, when using it, no changes are made to the connected devices
- Install with speech synthesis - installation with sound
We are also interested in the graphical install menu - installation with a graphical shell.

Installation on the SSD took no more than 10 minutes. After the installation is completed, they are not offered to use the network repository. Of course, we agree, after which the packages are automatically updated.
The next step is setting up the GRUB bootloader, in my case this is the only disk with one operating system, so we put the bootloader at the beginning of the only disk.
We reboot and log in as the root user and the password entered during the installation process, we are in the system.

Description of ALL kali linux utilities here – Kali Linux Tools Listing

01 - Information Gathering - First there are console and graphical utilities for collecting information, you can test the ports.


The most popular utilities are nmap (console) and zenmap, which is also with a graphical shell.
02 - The next section is Vulnerability Analysis, or our vulnerability scanners. For example, “OpenVAS”, as an analogue of the notorious Xspider scanner.

It takes quite a long time to install.

03 - Web application analysis - testing web applications.

04 - Database Assessement - everything for working with databases.

05 - Password Attacks - password guessing by hash, brute force.

06 - Wireless Attack - a set of utilities for auditing wireless networks.

07 - Reverse engineering - various debuggers and debuggers.

08 - Exploitation tool - exploitation of various exploits.

09 - Sniffing and spoofing utilities for working with traffic, mostly foreign.

10 - Post Exploitation another batch of exploits.

11 - "Forensic Tools" will help extract valuable information.

12 - Reporting tools - creating reports

13 - System services - start and stop application services.

In general, dozens of applications for brute force, guessing password hashes, searching for vulnerabilities in web servers, wi-fi networks, web applications.
To use this system, you will need experience using the linux OS and working with the console. Do not use this software for illegal purposes.
Article 272. Illegal access to computer information
1. Illegal access to legally protected computer information, that is, information on a machine medium, in an electronic computer (ECM), a computer system or their network, if this act entailed the destruction, blocking, modification or copying of information, disruption of the computer, system Computers or their networks, is punishable by a fine in the amount of up to 200 thousand roubles, or in the amount of the wage or salary, or any other income of the convicted person for a period of up to 18 months, or by corrective labor for a term of six months to one year, or by deprivation of liberty for a term of up to two years.
2. The same act committed by a group of persons by prior agreement or by an organized group, or by a person using his official position, as well as having access to a computer, a computer system or their network, is punishable by a fine in the amount of one hundred thousand to three hundred thousand rubles or the amount of wages or other income of the convicted person for a period of one to two years, or by corrective labor for a term of one to two years, or by arrest for a term of three to six months, or by deprivation of liberty for a term of up to five years.
If you have any questions, ask them on, or below in the comments.
The Kali Linux distribution has been gaining immense popularity lately. Hacking and security testing is becoming part of our culture and more and more people are interested in it. Perhaps the series "Mr. Robot" contributed to this process.
Kali Linux is one of the Linux distributions designed for hackers and security professionals. Therefore, it is not surprising that this series raises its popularity and many newcomers and people who have no knowledge of information security are trying to use this distribution as their main system. But Kali Linux is not designed for this at all. In today's article, we will look at what Kali Linux is, why we need it, and we will review Kali Linux.
Kali Linux was developed by Offensive Security, a security firm. It is based on Debian and contains the achievements of the digital forensics and security testing distribution BackTrack.
The first version of BackTrack was released in 2006, it combined several projects, the main purpose of which was penetration testing. The distribution was intended to be used as a LiveCD.
In 2012, a distribution such as BackTrack ceased to exist, and Kali Linux appeared in its place, which adopted all the advantages of the previous version and all the software. It was the result of a merger between two projects: WHAX and the Auditor Security Collection. Now the distribution is developing steadily and the efforts of developers are focused on fixing bugs and expanding the set of tools.
2. Purpose
The official website has the following description of the distribution: "Penetration Testing and Ethical Hacking Linux Distribution" or, in our opinion, a distribution for penetration testing and ethical hacking. Simply put, this distribution contains a variety of security and networking related tools that are aimed at computer security experts.
A Linux distribution is nothing more than a kernel and a set of basic utilities, applications, and default settings. Kali Linux does not provide anything unique in this regard. Most software can be easily installed on any other distribution, or even on Windows.
What makes Kali Linux different is that it is filled with tools and settings that are needed for security testing, and not for normal user experience. If you want to use Kali instead of the main distribution, you are making a mistake. This is a specialized distribution kit for solving a certain range of tasks, which means that solving tasks for which it was not intended will be more difficult, for example, the same search for programs. The capabilities of Kali Linux are focused on security testing.
3. Installation
You can download the installation image on the official website, you just need to select the architecture. After booting, be sure to check the disk for damage by comparing the SHA256 checksum. Since this distribution is intended for security testing, I don't want it to be broken in any way. How to do it is described in a separate article.
The rest of the installation of Kali Linux is not much different from Debian. Depending on the method and power of the computer, it can take from several minutes to half an hour. We examined everything in detail in the article.
4. Features
Many will be surprised, but the default user in Kali Linux is root. This is necessary because many programs need superuser rights to run. This is one of the reasons why you should not use Kali for everyday tasks such as surfing the Internet or using office applications.
If we talk about software, then all the supplied programs are focused on security. There are graphic programs, and there are terminal commands, and several basic utilities are included in the system, such as an image viewer, a calculator, and a text editor. But here you will not find office programs, readers, email programs and organizers.
Kali Linux is based on Debian, and nothing prevents you from installing the program from the repositories, for example, thunderbird for collecting mail. But browsing mail as root is not a good idea. Of course, no one is stopping you from creating an unprivileged user, but this is extra work.
On the Kali Linux login screen, you may see the motto "The quieter you become, the more you are able to hear" or "The quieter you become, the more you can hear". If you watch the packets sent to the network by the Debian system, you will notice that some packages are regularly sent to the network. Some of them are sent by the user's applications, others by background services.
For example, if you scan your Linux machine with , you may see several open ports. For example, it could be a never used VNC port and an HTTP server. Some of these programs are supplied by default, some you installed and forgot.
Kali Linux strives to be as quiet as possible. This is necessary to hide your presence in the attacked network and protect yourself from potential attacks. To achieve this goal, Kali disables many services that are enabled by default in Debian. Of course, you can install the desired service from the Debian repositories. For example, apache2:
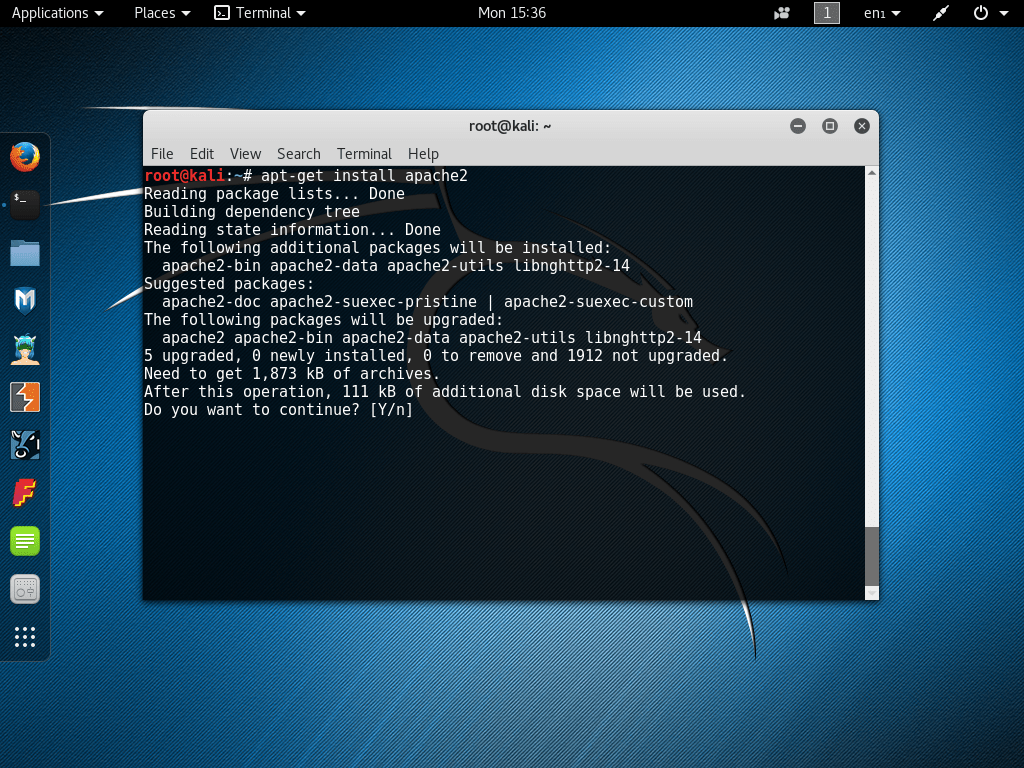
However, after that, the utility will not start automatically and will not be added to startup. If you need it, you will have to start it manually. With each reboot, all unnecessary services are disabled. It is possible to go around and whitelist the service in /usr/sbin/update-rc.d, but this is not entirely safe as you are exposing the system path. Nobody knows if there are vulnerabilities there.
Kali Linux is a specialized distribution, if only because it is designed to work in an aggressive environment. And if you installed a web server and a few other programs, and added them to startup, you may have already broken Kali and reduced its security.
5. Programs
As mentioned above, the Kali Linux distribution only contains specific security testing software. You can find a list of the most popular programs in the article. But there are not many programs necessary for normal work. And there is no guarantee that you will find them in the repositories, even if they are available in Debian.
You may want to add third-party repositories and application sources to install what you need, or add a repository that contains the latest version of the program. You can, but you don't have to. Even for Debian, this is not recommended, the developers call this phenomenon FrankenDebian and say that it can break the stability of the system.
With Kali Linux, things are even more complicated. You risk not only damaging the system, but also making it unsafe. Packages from the repositories are checked and contain additional changes, for example, the same Apache is not added to autoload. Third party packages will not have such precautions.
findings
Our overview of the features of Kali Linux is coming to an end. Whether you should choose this distribution or not depends on you and the tasks that you are trying to solve with the help of the system. If you only need a few tools, then it is better to choose some simpler distribution, such as Ubuntu or Debian. You can install all the necessary tools in it. The same option is better suited for new users.
But if you are already well versed in Linux and are willing to spend a lot of time to understand information security, perhaps this system is for you. But do not rush to install it on your computer. Use a virtual machine, then install it as an additional, second system.
Perhaps you disagree with the opinion described in the article, leave comments and tell us about your point of view.
There are several popular securty distributions that contain most of the popular penetration testing tools and applications. They are usually based on existing Linux distributions and are redesigned versions of them. This article will present the most famous of them.
Kali Linux
The most popular distribution to date. It is the successor to Backtrack Linux.Kali Linux is an incredibly powerful penetration testing tool that comes with over 600 security utilities such as Wireshark, Nmap, Armitage, Aircrack, Burp Suite, and more.
There are several types of this distribution for various platforms, such as ARM, virtualization systems, instances for carrying out attacks from mobile platforms - Kali Nethunter.
The distribution is currently a rolling release that ensures you always have the latest versions of the best penetration testing tools and utilities.

BlackArch
BlackArch Linux is built specifically for pentesters and security professionals. It supports i686 and x86_64 architectures. The installation kit now includes 1359 penetration testing utilities and their number is constantly increasing. Based on Arch Linux.The number of utilities is really quite impressive, but some of them have similar functionality and it can be quite difficult for a beginner to understand such a number of programs.

Parrot Security OS
An increasingly popular security distribution based on Debian-linux. Pretty easy to learn, suitable for both beginners and professionals. This distribution is aimed at both penetration testing and anonymous work on the Internet.A fairly lightweight and effective tool, many security specialists have found it a replacement for the increasingly “gluttonous” Kali, especially since Parrot uses the Kali repositories for updates.

backbox
BackBox is an Ubuntu-based lightweight distribution. In a direct comparison with Kali, it will lose on many counts. It does not have so many different tools, utilities and frameworks available right out of the box. There are no kernel optimizations and other tweaks.Thanks to the lightweight XFCE backbox, Linux is more suitable for everyday use as a workhorse on your personal computer. There is a mode - Anonymous mode - all system traffic is passed through the TOR proxy. The startup script changes the system's MAC address and hostname, and when the mode is turned off, all temporary files are deleted using the integrated BleachBit package.
Backbox Linux can be a great alternative to Kali Linux for those looking for a balance between functionality and everyday usability.

Pentoo Linux
Pentoo is a security distribution based on the popular Gentoo Linux distribution that Pentoo developers are fans of. Contains many security utilities.One of the features is native support for Hardened Gentoo - several changes in the compiler and kernel that increase the overall security of the system from hacking.

Network Security Toolkit
The Network Security Toolkit is one of many live CD-type Linux distributions aimed at network security analysis. NST gives administrators easy access to a wide variety of open network applications, many of which are included in insecure.org's top 100 security tools. Based on Fedora Linux.Possessing a balanced set of network monitoring, analysis and security tools, it can give a clear advantage to the network administrator to control the security of the infrastructure entrusted to him.

DEFT Linux
This distribution is developed on the Lubuntu platform and is equipped with a user-friendly graphical interface. In addition, a set of specialized utilities has been added to the product, starting with antiviruses, search engines for information in the browser cache, network scanners and utilities for detecting rootkits and ending with tools needed to search for data hidden on the disk.The main purpose is to carry out forensic events - to analyze the consequences of hacking computer systems, identify lost and compromised data, and also to collect the so-called. digital evidence of cybercrime.

Samurai Web Security Framework
The main purpose of this distribution is penetration testing of various web applications.Delivered as a virtual machine image containing the most popular Open Source utilities for collecting information and conducting various attacks on web applications.

Pentest box
PentestBox is not like other security distributions that run on virtual machines. It would not be entirely correct to call this assembly a distribution, it is rather a set of *nix-like utilities that work in a Windows environment.It has its own shell, the interface is made in the form of a command line, it contains a large number of utilities, the list of which can be independently supplemented / customized.
If you are a Windows user and you are afraid of installing virtual machines or Linux, you can try to work with this shell.

Santoku Linux
The distribution is based on Ubuntu linux. Presented only as an X64 platform.This assembly is intended for mobile devices and applications analysis - security analysis, data extraction, reverse engineering, forensics, and also contains development tools.

WiFiSlax
This is a specialized distribution with a collection of tools for checking the security of WiFi network systems and conducting forensic analysis. The distribution is based on Slackware linux.Currently, it is one of the most commonly used WiFi network audit tools, it includes most of the popular wireless network security analysis utilities, and is supported by most network card manufacturers.

There are several popular securty distributions that contain most of the popular penetration testing tools and applications. They are usually based on existing Linux distributions and are redesigned versions of them. This article will present the most famous of them.
Kali Linux
The most popular distribution to date. It is the successor to Backtrack Linux.Kali Linux is an incredibly powerful penetration testing tool that comes with over 600 security utilities such as Wireshark, Nmap, Armitage, Aircrack, Burp Suite, and more.
There are several types of this distribution for various platforms, such as ARM, virtualization systems, instances for carrying out attacks from mobile platforms - Kali Nethunter.
The distribution is currently a rolling release that ensures you always have the latest versions of the best penetration testing tools and utilities.

BlackArch
BlackArch Linux is built specifically for pentesters and security professionals. It supports i686 and x86_64 architectures. The installation kit now includes 1359 penetration testing utilities and their number is constantly increasing. Based on Arch Linux.The number of utilities is really quite impressive, but some of them have similar functionality and it can be quite difficult for a beginner to understand such a number of programs.

Parrot Security OS
An increasingly popular security distribution based on Debian-linux. Pretty easy to learn, suitable for both beginners and professionals. This distribution is aimed at both penetration testing and anonymous work on the Internet.A fairly lightweight and effective tool, many security specialists have found it a replacement for the increasingly “gluttonous” Kali, especially since Parrot uses the Kali repositories for updates.

backbox
BackBox is an Ubuntu-based lightweight distribution. In a direct comparison with Kali, it will lose on many counts. It does not have so many different tools, utilities and frameworks available right out of the box. There are no kernel optimizations and other tweaks.Thanks to the lightweight XFCE backbox, Linux is more suitable for everyday use as a workhorse on your personal computer. There is a mode - Anonymous mode - all system traffic is passed through the TOR proxy. The startup script changes the system's MAC address and hostname, and when the mode is turned off, all temporary files are deleted using the integrated BleachBit package.
Backbox Linux can be a great alternative to Kali Linux for those looking for a balance between functionality and everyday usability.

Pentoo Linux
Pentoo is a security distribution based on the popular Gentoo Linux distribution that Pentoo developers are fans of. Contains many security utilities.One of the features is native support for Hardened Gentoo - several changes in the compiler and kernel that increase the overall security of the system from hacking.

Network Security Toolkit
The Network Security Toolkit is one of many live CD-type Linux distributions aimed at network security analysis. NST gives administrators easy access to a wide variety of open network applications, many of which are included in insecure.org's top 100 security tools. Based on Fedora Linux.Possessing a balanced set of network monitoring, analysis and security tools, it can give a clear advantage to the network administrator to control the security of the infrastructure entrusted to him.

DEFT Linux
This distribution is developed on the Lubuntu platform and is equipped with a user-friendly graphical interface. In addition, a set of specialized utilities has been added to the product, starting with antiviruses, search engines for information in the browser cache, network scanners and utilities for detecting rootkits and ending with tools needed to search for data hidden on the disk.The main purpose is to carry out forensic events - to analyze the consequences of hacking computer systems, identify lost and compromised data, and also to collect the so-called. digital evidence of cybercrime.

Samurai Web Security Framework
The main purpose of this distribution is penetration testing of various web applications.Delivered as a virtual machine image containing the most popular Open Source utilities for collecting information and conducting various attacks on web applications.

Pentest box
PentestBox is not like other security distributions that run on virtual machines. It would not be entirely correct to call this assembly a distribution, it is rather a set of *nix-like utilities that work in a Windows environment.It has its own shell, the interface is made in the form of a command line, it contains a large number of utilities, the list of which can be independently supplemented / customized.
If you are a Windows user and you are afraid of installing virtual machines or Linux, you can try to work with this shell.

Santoku Linux
The distribution is based on Ubuntu linux. Presented only as an X64 platform.This assembly is intended for mobile devices and applications analysis - security analysis, data extraction, reverse engineering, forensics, and also contains development tools.

WiFiSlax
This is a specialized distribution with a collection of tools for checking the security of WiFi network systems and conducting forensic analysis. The distribution is based on Slackware linux.Currently, it is one of the most commonly used WiFi network audit tools, it includes most of the popular wireless network security analysis utilities, and is supported by most network card manufacturers.

The book is a systematic collection, including translations of English-language resources, books and websites dedicated to the topic penetration testing and the authors' own experience.
Official description for the book:
Kali Linux is advanced linux distribution for penetration testing and security auditing. The information in this book is intended only for evaluation or penetration testing of their own tei.
To test third party networks, get written permission.
"Penetration testing (slang Pentest) - a method for evaluating the security of computer systems or networks by means of intruder attack simulation." - WiKi.
All responsibility for the implementation of the actions described in the book lies with you. Remember that for illegal actions, liability is provided, up to criminal.
The book consists of 8 parts, which include 62 chapters. Everything is explained in detail with examples. The book uses the most up-to-date information to date.
1. General information and installation of Kali Linux
- What is Kali Linux?
- How to install Kali Linux: detailed instructions for installing on a computer and in a virtual machine
- Installing the VirtualBox Guest Additions for Kali Linux 2.0
- How to install Kali Linux on a flash drive and on an external drive (the easy way)
- Top 10 Tips on What to Do After Installing Kali Linux 2.0
- VMware tools in a Kali guest
- How to enable VPN on Kali Linux - resolving the problem of not being able to add a VPN
- Checking and restoring repositories in Kali Linux from the command line
- How to change desktop environment in Kali Linux
- How to add/remove regular (non-root) user in Kali Linux
- How to reset root password in Kali Linux
- Restoring GRUB in Kali Linux after upgrading to Windows 10
- Increasing Your Online Anonymity with Tor in Kali Linux
2. Overview of Kali Linux Tools
- An overview of the Kali Linux tools sections. Part 1. Brief description of all sections
- An overview of the Kali Linux tools sections. Part 2. Tools for collecting information
- The best hacking programs
- Exploit database from Offensive Security (creators of Kali Linux)
3. Wireless Penetration Testing
- Best Compatible Kali Linux USB Wi-Fi Adapters
- Wifi password cracking (WPA/WPA2) using pyrit and cowpatty in Kali Linux
- Cracking Wifi WPA/WPA2 Passwords Using Reaver
- Reaver fork modification - t6x - to use the Pixie Dust attack
- Cracking WPA2/WPA Passwords with Hashcat on Kali Linux (Wi-Fi Password Mask Attack)
- Wifite mod with Pixiewps support
- Hacking Wi-Fi Networks: Tools That Didn't Make it to Kali Linux
- Router Scan by Stas'M on Kali Linux (hacking routers and Wi-Fi on an industrial scale)
- Fixing Wifi_Jammer and Wifi_DoS in WebSploit
- Wireless network stress test with Wifi_Jammer: how to jam Wi-Fi
- Stress test of a wireless network with Wifi_DoS: how to dosit Wi-Fi
4. Network stress tests
- Network stress test (DoS website) with SlowHTTPTest in Kali Linux: slowloris, slow body and slow read attacks in one tool
- Network stress test: DoS a website on Kali Linux with GoldenEye
- Network stress test with Low Orbit Ion Cannon (LOIC)
- Network stress test: DoS using hping3 and IP spoofing in Kali Linux
5. Vulnerability analysis in web applications
- WhatWeb instructions: how to find out the site engine in Kali Linux
- SQL injection: a simple explanation for beginners (part 1)
- Using SQLMAP on Kali Linux: Hacking Websites and Databases via SQL Injection
- Hack plugins for Firefox
- Scanning for WordPress Vulnerabilities: WPScanner and Plecost
- Plecost 1.0.1 New Version - WordPress Vulnerability Finder
- Working with W3af in Kali Linux
- ZAProxy: Web Application Penetration Testing
- How to run Metasploit Framework in Kali Linux 2.0
- How to run Metasploit Framework in Kali Linux 1.1
- Metasploit Exploitation Framework and searchsploit - how to search and how to use exploits
- DIRB: Find hidden directories and files on websites
- Search for admin sites with Kali Linux
6. Vulnerability analysis in operating systems and server software
- Vulnerability Scanning with OpenVAS 8.0
- Armitage Tutorial: Automatic Search and Check for Exploits in Kali Linux
- How to Scan Linux for Rootkits with rkhunter
- Linux security audit
- Installing Linux Malware Detect (LMD) on Linux
- How to LEARN Windows password?
7. Scanning networks. Interception of data in networks
- Network emulation from multiple computers on one computer
- How to Use NMAP Security Scanner on Linux
- Book on Nmap in Russian
- Cracking a Website Password Using WireShark (and Protecting Against It)
- FTP-Map: we determine the software and its version for FTP servers and look for exploits for them
- ZMap or How to Scan All IPv4 Addresses in the World in 45 Minutes
- 8. Attacks on passwords. Bruteforcing
- Dictionary attack wordlists: passwords, usernames, directories
- PW-Inspector: select passwords that match the criteria
- THC-Hydra: Very Fast Net Login Cracker (Part One)
- Bruteforcing websites with Hydra (part two of the Hydra guide)
- Crunch - Password Generator: Usage Basics and Practical Examples
- BruteX: a program for automatic brute force of all services
JavaScript is disabled in your browser