USB mouse pinout by wire colors. Pinout and wiring of USB connectors - basic information. Three versions of USB
USB (universal serial bus) - The USB data transfer interface is ubiquitous today, used in almost all devices - phones, PCs, MFPs, tape recorders and other devices are used both for data transfer and for charging phone batteries.
Types of USB connectors.
There are many different types of USB connectors. All of them are shown below.
Type A- active, powering device (computer, host). Type B- passive, connected device (printer, scanner)
USB cable pinout by color.
Usb 2.0 pinout.

USB is a serial bus. It uses 4 shielded wires: two for power (+5v & GND) and two for differential data signals (labeled D+ and D-).

usb micro
USB micro has been used since 2011 in phones, MP3s and other devices. Micro is a newer version of the mini connector. It has an advantage in the connection of connectors, the connector is connected tightly to the plug and provides a tight connection.
micro usb pinout- desoldering micro-USB is now considered the most common type of repair of this kind of device. Surely you have already encountered such a situation when you currently need a USB adapter, but it was not at hand. The circumstances are different - the device has failed, it has disappeared somewhere, it is not for sale, its length is not enough, and so on. If you are familiar with the technique of how micro usb pinout is performed, then you can solve this problem with your own hands at home.
USB WIRE COLORS required for repairing USB CABLES.
| Conclusion | Name | Wire color | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | +5V | |
| 2 | D- | Data - | |
| 3 | D+ | Data + | |
| 4 | GND | Earth |
The heterogeneity of USB 2.0 connectors is shown in the figure below.
The name of one or another connector is indicated by the indexes of the letter designation.
Connector Model:
A - active action, power source - personal computer, USB Host Controller
B - passive action, additional equipment - computer printer or scanner
Connector type:
M - male connector
F - socket
Connector dimensions:
no designation index
MINI
MICRO
USB MICRO-BM- male connector (M) is used for switching with a passive device (B); micro dimensions.
Micro usb pinout - sockets and pin headers
The purpose of the wires in the USB connector is as follows:
- Red wire- + 5v positive voltage in relation to the "ground". Limit current - 0.5A
- White wire D-(-Data)
- Green wire D+(+Data)
- Black wire GND - common bus, "ground", "case" - no voltage
Mini-micro connectors are provided with five pins:
- Red
- White D-
- Green D+
- ID - in connectors "B" is not connected; in connectors "A" is shorted to GND to ensure the operation of "OTG"
- Black color GND "ground"
In addition to all of the above, a USB cable can have a core without insulation Shield - a case, a shielding braid. This conductor is not assigned identification.
Correct perception of the connectors in the pictures:
All tables with the image of the connector, which is shown from its outer working side, and not from the side of the solder pads. Components acting as insulating elements in the diagram are light gray, segments made of metal are marked in dark gray, voids in the connector are marked in white.
USB desoldering technique
Standard USB does not cause any difficulties, all you need to do is take the drawing of the front side of the connector, geometrically transformed into a mirror image and you can solder it.
The pinout of the MINI and MICRO USB male connectors is shown in the image below:
Five pin connectors MINI and MICRO. In connector variant "B", the fourth pad is not used. In option "A", the fourth pad is shorted to the GND bus. And the GND contact itself has a digital designation No5.
The USB interface is a popular form of technology communication on mobile and other digital devices. Connectors of this kind are often found on personal computers of various configurations, peripheral computer systems, cell phones, etc.
A feature of the traditional interface is a small area USB pinout. Only 4 pins (contacts) + 1 ground shield line are used for operation. True, the latest more advanced modifications (USB 3.0 Powered-B or Type-C) are characterized by an increase in the number of working contacts. What we will talk about in this material. We will also describe the structure of the interface and the features of the cable desoldering on the pins of the connectors.
The abbreviation "USB" is an abbreviation, which in its entirety is read as "Universal Series Bus" - a universal serial bus, thanks to which high-speed digital data exchange is carried out.
The versatility of the USB interface is noted:
- low power consumption;
- unification of cables and connectors;
- simple logging of data exchange;
- high level of functionality;
- wide support for drivers of different devices.
What is the structure of the USB interface, and what types of USB technological connectors exist in the modern world of electronics? Let's try to figure it out.
Technological structure of the USB 2.0 interface
Connectors related to products included in the 1.x - 2.0 specification group (created before 2001) are connected to a four-wire electrical cable, where two conductors are supplying and two more are transmitting data.
Also, in specifications 1.x - 2.0, the decoupling of service USB connectors involves connecting a shielding braid - in fact, the fifth conductor.
This is how the physical performance of normal USB connectors related to the second specification looks like. On the left are the executions of the "father" type, on the right are the executions of the "mother" type and the pinout corresponding to both options
The existing versions of the universal serial bus connectors of the marked specifications are represented by three options:
- Normal- type "A" and "B".
- Mini- type "A" and "B".
- Micro- type "A" and "B".
The difference between all three types of products lies in the design approach. While normal connectors are designed for use on stationary equipment, mini and micro connectors are made for use in mobile devices.

This is how the physical design of connectors of the second specification from the “mini” series looks like and, accordingly, the labels for Mini USB connectors - the so-called pinout, based on which the user makes a cable connection
Therefore, the last two types are characterized by a miniature design and a slightly modified shape of the connector.
Pinout table for standard type "A" and "B" connectors
Along with the execution of "mini-A" and "mini-B" connectors, as well as "micro-A" and "micro-B" connectors, there are modifications of "mini-AB" and "micro-AB" connectors.
A distinctive feature of such designs is the execution of the soldering of the USB conductors on a 10-pin contact pad. However, in practice, such connectors are rarely used.
Pinout table for Micro USB and Mini USB connectors type "A" and "B"
Technological structure of USB 3.x interfaces
Meanwhile, the improvement of digital equipment by the time of 2008 led to obsolescence of specifications 1.x - 2.0.
These types of interface did not allow the connection of new equipment, for example, external hard drives, in such a way that a higher (more than 480 Mbit / s) data transfer rate was provided.
Accordingly, a completely different interface was born, marked with the 3.0 specification. The development of the new specification is not only characterized by increased speed, but also provides increased current - 900 mA versus 500 mA for USB 2/0.
It is clear that the advent of such connectors provided service for a larger number of devices, some of which can be powered directly from the universal serial bus interface.

Modification of USB 3.0 connectors of different types: 1 - version "mini" type "B"; 2 - standard product type "A"; 3 - development of the "micro" series of type "B"; 4 - standard version of type "C"
As you can see in the picture above, the interfaces of the third specification have more working contacts (pins) than the previous - the second version. However, the third version is fully compatible with the "two".
In order to be able to transmit signals at a higher speed, the designers of the third version equipped with an additional four data lines and one line of a neutral contact wire. Supplemented contact pins are located in a separate row.
Table of designation of pins of connectors of the third version for unsoldering the USB cable
| Contact | Execution "A" | Version "B" | Micro B |
| 1 | Meals + | Meals + | Meals + |
| 2 | Data - | Data - | Data - |
| 3 | Data + | Data + | Data + |
| 4 | Earth | Earth | Identifier |
| 5 | stdA_SSTX - | stdA_SSTX - | Earth |
| 6 | StdA_SSTX+ | StdA_SSTX+ | stdA_SSTX - |
| 7 | GND_DRAIN | GND_DRAIN | StdA_SSTX+ |
| 8 | StdA_SSRX- | StdA_SSRX- | GND_DRAIN |
| 9 | StdA_SSRX+ | StdA_SSRX+ | StdA_SSRX- |
| 10 | – | – | StdA_SSRX+ |
| 11 | Shielding | Shielding | Shielding |
Meanwhile, the use of the USB 3.0 interface, in particular the “A” series, turned out to be a serious flaw in the design plan. The connector has an asymmetric shape, but the connection position is not specifically indicated.
The developers had to modernize the design, as a result of which, in 2013, the USB-C option appeared at the disposal of users.
Upgraded USB 3.1 connector
The design of this type of connector involves duplication of working conductors on both sides of the plug. There are also several redundant lines on the interface.
This type of connector has found wide application in modern mobile digital technology.

The location of contacts (pins) for the USB-C type interface, which belongs to the series of the third specification of connectors designed for communications of various digital equipment
It is worth noting the characteristics of USB Type-C. For example, the speed parameters for this interface show a level of 10 Gbps.
The design of the connector is made in a compact design and provides a symmetrical connection, allowing the connector to be inserted in any position.
Pinout table conforming to Specification 3.1 (USB-C)
| Contact | Designation | Function | Contact | Designation | Function |
| A1 | GND | grounding | B1 | GND | grounding |
| A2 | SSTXp1 | TX+ | B2 | SSRXp1 | RX+ |
| A3 | SSTXn1 | TX- | B3 | SSRXn1 | RX- |
| A4 | Tire + | Meals + | B4 | Tire + | Meals + |
| A5 | CC1 | CFG channel | B5 | SBU2 | PPD |
| A6 | Dp1 | USB 2.0 | B6 | Dn2 | USB 2.0 |
| A7 | Dn1 | USB 2.0 | B7 | Dp2 | USB 2.0 |
| A8 | SBU1 | PPD | B8 | CC2 | CFG |
| A9 | Tire | Nutrition | B9 | Tire | Nutrition |
| A10 | SSRXn2 | RX- | B10 | SSTXn2 | TX- |
| A11 | SSRXp2 | RX+ | B11 | SSTXp2 | TX+ |
| A12 | GND | grounding | B12 | GND | grounding |
The next level of the USB 3.2 specification
Meanwhile, the process of improving the universal serial bus is actively continuing. At the non-commercial level, the next specification level, 3.2, has already been developed.
USB 3.2 type interfaces are said to promise double the performance of the previous design.
The developers managed to achieve such parameters by introducing multiband channels through which transmission is carried out at speeds of 5 and 10 Gbps, respectively.

Similar to "Thunderbolt", USB 3.2 uses multiple lanes to achieve total bandwidth, rather than trying to sync and run the same channel twice
By the way, it should be noted that the compatibility of the future interface with the existing USB-C is fully supported, since the Type-C connector (as already noted) is endowed with spare contacts (pins) that provide multi-band signal transmission.
Features of cable desoldering on connector pins
Some special technological nuances of soldering cable conductors on the contact pads of the connectors are not noted. The main thing in such a process is to ensure that the color of the preliminary cable conductors matches a specific contact (pin).

Color coding of conductors inside the cable assembly used for USB interfaces. Shown from top to bottom, respectively, are the cable conductor colors for specifications 2.0, 3.0 and 3.1.
Also, if modifications of obsolete versions are desoldered, the configuration of the connectors, the so-called “father” and “mother”, should be taken into account.
The conductor soldered on the “male” contact must match the soldering on the “mother” contact. Take, for example, the option of desoldering a cable using USB 2.0 pins.
The four working conductors used in this variant are usually marked with four different colors:
- red;
- white;
- green;
- black.
Accordingly, each conductor is soldered to a contact pad marked with a connector specification of a similar color. This approach greatly facilitates the work of an electronics engineer, eliminates possible errors in the desoldering process.
A similar soldering technique is applied to connectors of other series. The only difference in such cases is the greater number of conductors that have to be soldered. To simplify your work, it is convenient to use a special tool - a reliable soldering iron for soldering wires at home and for stripping insulation from the ends of the wires.
Regardless of the connector configuration, shield conductor soldering is always used. This conductor is soldered to the corresponding pin on the connector, Shield - protective screen.
There are frequent cases of ignoring the protective screen, when "specialists" do not see the point in this conductor. However, the lack of a shield drastically reduces the performance of the USB cable.
Therefore, it is not surprising when, with a significant cable length without a screen, the user gets problems in the form of interference.

Desoldering the connector with two conductors for organizing a power line for the donor device. In practice, different wiring options are used, based on technical needs.
Soldering the USB cable is allowed in different ways, depending on the configuration of the port lines on a particular device.
For example, in order to connect one device to another in order to obtain only a supply voltage (5V), it is enough to solder only two lines on the corresponding pins (contacts).
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video below explains the main pinout points of the 2.0 series connectors and others, visually explains the individual details of the soldering procedures.
With complete knowledge of Universal Serial Bus connector pinouts, you can always deal with a technical problem related to wire defects. Also, this information will definitely come in handy if you need to non-standardly connect some digital devices.
Would you like to supplement the above material with useful comments or valuable tips for self-soldering? Write comments in the block below, add, if necessary, unique photographic materials.
Do you have any questions after reading the article? Ask them here - our experts and competent site visitors will try to clarify incomprehensible points.
The USB connector appeared twenty years ago and was originally intended for use in household appliances. It has now gained quite a lot of popularity also in professional equipment. Nevertheless, its “household” roots are clearly manifested in the fact that all popular gadgets without exception are supplied with this type of plug-in connector.
The original version of the connector differed in dimensions, not quite suitable for installing its sockets in portable devices in a pocket format. To eliminate this shortcoming, miniUSB and microUSB variants were created, which made it possible to implement the main functions of the connector and, at the same time, favorably differed from the prototype by noticeably better weight and size characteristics.
Characteristic features of the microUSB connector
The microUSB connector contains five pins, each with an insulated wire soldered to it. The correct orientation of the plug when connected to the outlet is determined by the use of characteristic smoothed bevels of one of the upper faces of the shielding skirt. The male connector pins are numbered from 1 to 5 with natural numbering from right to left, as shown in the figure. Unsoldering the micro usb connector and the purpose of its individual contacts are given in the table.
Micro usb pinout by color
The braided shield of a cable is also considered a wire. It is not displayed on a separate contact.

Unsoldering the micro usb connector for charging
Connector repair and cable manufacturing
The good performance properties of the cable and device part of the micro USB connector, combined with the low cost of the connecting cable and its wide distribution, lead to the fact that repairs of this accessory are relatively rare. However, in the case of its installation of a new nest, due to the well-thought-out design, it is not a big problem even despite its rather miniature size. Of the features, attention should be paid to the accuracy and expediency of additional protection of the soldering point, for example, with non-conductive varnish.
USB 2.0 connectors - wiring.
In this article, we want to tell you about the USB 2.0 connectors used in various electronic devices. They still have not lost their relevance, despite the release of a faster USB 3.0, which we will talk about a little later in the next article on this topic.
The abbreviation USB stands for Universal Serial Bus, translated as Universal Serial Bus.
The picture below shows USB 2.0 connectors (view from the side of the working part, please note that this is not the solder side):

When desoldering, select the desired connector, view it in a mirror image, and solder the wires according to their color. The colors of the cable cores are described below.
As you can see, there are indexes in the names of the connectors (USB, USB mini, USB micro). The first letter of the index determines the connector type:
● A - active power supply connector (host, computer connector, etc.)
● B – connector of a passive device connected to an active one (connectors of printers, scanners, etc.)
The second letter of the index determines the “gender” of the connector:
● M - from the English word male - that is, a plug - that is, a “Daddy” connector
● F - from the English word female - that is, the nest - that is, the “Mom” connector
Just USB, mini or micro tells us the size of the connector. Here's an example:
USB mini AM is a male connector (male) for connection to a mini active power supply device.
Now let's analyze the pinout (wiring) of the USB connectors.
The USB cable has 4 wires:

● 1 - Red wire - VBUS - +5 Volts with a maximum current of 0.5 Amps.
● 2 - White wire - D- (minus Data).
● 3 - Green wire - D+ (plus Data)
● 4 - Black wire - GND - common wire, negative, "ground"
Mini & Micro connectors 5-pin. The breakdown is as follows:

● 1 - Red wire - VBUS.
● 4 - Blue wire - not used in connectors with index “B”, in connectors with index “A” it is connected to the black wire (GND) to support the “OTG” function.
● 5 - Black wire - GND.
When cutting a cable, you can sometimes find another core without insulation - Shield - a braid that shields the core, a case. This one didn't have a number.
The pinout of the USB Mini and USB Micro connectors is shown in the following figure:

When unsoldering the data cable for connecting a mobile phone, smartphone or tablet to a computer, the 4th contact remains empty. When unsoldering an OTG cable, for example, to connect a USB flash drive to a smartphone, the 4th pin must be connected to the 5th (GND).
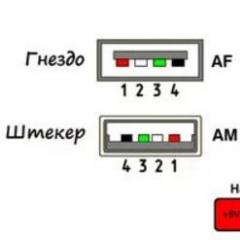
USB mouse. Connector pinout:
● 2 - White wire - Data minus.
● 3 - Green wire - Data plus.
● 4 - Black wire - GND.
These are the standard USB mouse cable wire colors, but depending on the manufacturer, these colors may be different from the above. For example, in Chinese-made mice such as Jusajoa X-7, many similar colors of wires can be as follows:
● 1 - Orange wire - VBUS.
● 2 - Green wire - Data minus.
● 3 - Blue wire - Data plus.
● 4 - White wire - GND.
Motherboard connector pin assignment for USB 2.0 cable

OTG - what is it?
Above we mentioned the OTG function, so now let's figure out a little what it is.
OTG stands for “On The Go”, which translates as “On the go”, that is, it allows you to connect various peripheral devices via USB without connecting to a computer. Sometimes this connection is called USB-Host. For example, you can connect a flash drive directly to a mobile phone or tablet as a full-fledged PC, connect a keyboard or mouse to a gadget, but if this gadget supports this peripheral equipment. Through USB-OTG, you can connect a camera and a photo printer, a camera to a smartphone, a mobile phone to a printer, etc.
There are a number of restrictions on this type of connection:
● Legacy mobile phones do not support USB-OTG.
● To connect a flash drive via USB-OTG, the format must be FAT32.
● The maximum size of the flash drive depends on the hardware capability of the phone.
● HDD - also in FAT32, and its power supply will require a separate source.
In shops with mobile phones, smartphones and other gadgets, you can find ready-made OTG cables, and if you wish, you can purchase a ready-made adapter. Suppose you need to connect a flash drive to a mobile phone with a USB micro connector, this will require a USB_AF - USB_AM micro adapter. A flash drive is connected to the USB-AF connector, and the USB-AM micro connector plug to the phone, respectively. The appearance of the OTG MICRO USB THROW OTG/USB adapter is shown in the following image:

Connecting a flash drive to a tablet is exactly the same, only instead of a USB micro connector, the adapter should have a USB mini.
And so, you already understood that a regular USB cable differs from USB-OTG in that the 4th pin of the connector is not used in the usual one, and a jumper is installed between the 4th and 5th pins in OTG. It is by the presence of a jumper in USB mini or micro that a phone, smartphone or tablet determines that you are going to connect peripherals to it. And if you suddenly decide to make a connection using a regular cable, then the gadget to which you are going to connect will ignore the connected flash drive, and will itself be a passive device. The picture below shows the USB-OTG micro cable connector:

Connecting gadgets.