What does it mean to make a disk dynamic. Convert to dynamic disk - what does it mean. How to make a dynamic disk basic without data loss
As such, there are two types of computer hard drives: primary and dynamic disks. Basic drives are commonly used media with Windows. They contain partitions - primary partitions and logical drives that are usually formatted with a file system. Dynamic disks provide the ability to create fault-tolerant volumes, and can even span multiple disks - basic disks cannot. We can easily convert basic disk to dynamic on our Windows XP, 2003, 2008, Windows 7, Windows 8 operating systems, but it is quite difficult to convert dynamic disk to basic. Why is this happening? This is because Windows disk manager does not support converting a dynamic disk that contains volume(s) or partition(s) in a basic disk, and it will only allow you to convert those disks that do not contain volumes or partitions.
Dynamic disks and basic disks
Basic disk: a physical disk that can be used in MS-DOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System) and all Windows-based operating systems. It can contain up to 4 primary partitions, or 3 primary partitions and 1 secondary partition, which contains multiple logical partitions.
Dynamic Disk: this is also a kind of disk, the function of which is similar to the main partition on a basic disk. However, it can break up and share data between disks. For example, a dynamic disk may actually consist of a storage space that is divided into two disks. In addition, you can copy data between disks to a dynamic disk in case of some disk corruption. This feature needs larger drives, but is more reliable.
The Windows operating system supports two types of disks: basic disk and dynamic disk. Basic disks are used to manage data on disks using primary partitions, extended partitions, and logical partitions; while the dynamic disk concept was introduced by Microsoft starting with Windows 2000 and added to Disk Management. Dynamic disk storage uses disk space, with benefits such as the ability to create volumes and occupy devices across multiple disks. Therefore, an increasing number of users want to use a dynamic disk instead of the usual one, and are looking for methods to convert their basic disks to dynamic ones. However, since some Windows operating systems (Windows NT, MS-DOS and all Microsoft Home Edition operating systems, Vista Home Basic Edition, Windows 7 Home Basic Edition…) do not support dynamic disk, in some situations you must convert a dynamic disk to base. Unfortunately, Windows does not provide services for such needs. However, users can use third party software such as AOMEI Partition Assistant to make this conversion. With AOMEI Partition Assistant, you can easily convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk without data loss, and in the same way, we could also easily convert a basic disk to a dynamic one, either using the built-in Disk Management snap-in window or partition assistant.
Most home PCs are configured with basic disks, however, IT pros tend to prefer dynamic disks because they offer more functionality and improve reliability and performance. So far, home versions of the Windows operating system support basic Enterprise/Pro/Ultimate disks in various versions of the Windows operating system, and also support dynamic disks. Microsoft lists the operations that can be performed on each of these types.
Works that can be performed on basic and dynamic disks:
- Check the properties of the disk, section "Properties" and "Volume Properties".
- Sets the drive letter assignment for a disk volume or partitions.
- Support for both MBR and GPT partition styles.
- Convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk or a dynamic disk to a basic disk.
Operations that can only be performed on dynamic disks:
- Create and delete simple, spanned, striped, mirrored, and RAID-5 volumes.
- Make extensions to a simple or spanned volume.
- Delete a mirror from a mirrored volume.
- Make a mirror volume break in two volumes.
- Repair a mirrored or RAID-5 volume.
- Ability to activate a missing or disabled drive.
Converting a Basic Disk to a Dynamic Disk
Before starting this process, you should be aware that you may lose data as a result of this operation, so it is extremely important that you back up your data to an external hard drive first. So let's get started only if you know what you're doing and be careful.
If you are using a basic disk as your shadow copy storage, in order to avoid data loss and you intend to convert the basic disk to a dynamic disk, it is important to take the following precautions. If the disk does not have a boot volume where the source files are stored, before converting the disk, you must first unmount and remove the volume containing the source files that contains the shadow copies on a dynamic disk. You must bring the volume containing the original files back within 20 minutes, otherwise, you will lose the data stored in the existing shadow copies. If the shadow copies are on a boot volume, you can convert the disk to dynamic without losing the shadow copies.
Using the user interface
To convert to Windows 8.1, open the WinX menu and select Disk Management. Right-click on the disk and select "Convert to Dynamic Disk". You will be prompted to check the disk again and click on the "Convert later" button. The process will start and the disk will be converted to a dynamic disk.
Using the command line
Open an elevated command prompt, type diskpart and press Enter.
Now type in select diskn and press Enter.
Enter the following type convert dynamic and press Enter.
Convert dynamic disk to basic disk
Using Disk Management
Using Disk Management - To convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk, right-click on the volume you want to convert to a basic disk, and for each volume on the disk, select the Delete Volume command. When all volumes on the disk are deleted, right-click on the disk and select "Convert to Basic Disk". The conversion operation will start.
Using CMD
Open a command prompt and type diskpart and press Enter.
Enter the following type list disk and write down the disk number, the disk you want to convert to basic. Now enter the data and press the Enter key, one by one:
- Enter type select disk
- Enter type detail disk
- For each volume on the disk, enter the type select volume=<номер тома> and then type delete volume.
- Enter type select disk
Finally type inconvert basic and press Enter. The conversion operation will start.
Remember that before you perform any of these operations, you should always make a backup. As well as never convert the basic disk containing the operating system to a dynamic disk, as this may make the system unbootable.
dynamic disk is a hard disk formatted in a non-standard way. The principle and algorithm of such formatting belongs to Microsoft. A dynamic format involves storing additional metadata on the disk, which is why even with normal formatting, Windows always (always) reserves about disk space. It is understood that sooner or later the user will want to make a dynamic disk out of a regular disk.
In this case, it is important for the user to always remember one thing.
There is no way to convert a dynamic disk to a regular (basic) disk without reformatting the entire disk.
In fact, the transformation of a regular (so-called "basic") disk into a dynamic disk is its preparation for participation in a Windows software RAID.
dynamic volume are partitions on dynamic disks linked into a software RAID. In other words, that's what Microsoft people call their software RAID arrays.
Using dynamic disks is the only way to do software RAID using Windows itself. At the same time, information about the RAID structure is stored on the disk itself (in fact, this requires an additional 8 megabytes of disk space).
This software RAID is very easy to create. Just enter the console snap mmc"Disk Management", then everything is intuitive. But, as easy as it is to create, it is so difficult to restore it later. More precisely, it is almost impossible.
Never use dynamic disks for data storage.
More
The best information on dynamic disks was provided by Chris Kaspersky aka mice See The Whole Truth About Dynamic Disks. I will quote only selected quotes.
Dynamic disks appeared in NT 3.51 (according to other sources - in NT 4.0), only there they were called multidisk and were ordinary software RAIDs that are widespread in the UNIX world.
Multidisk configuration information was stored in the registry and a system crash resulted in the loss of all data. The same applied to a full system reinstall or trying to move the hard drive to a system from a different NT. These shortcomings neutralized all the advantages of multidiscs, significantly limiting the scope of their application.
Starting with W2K, Microsoft slightly improved the multidisk manager and now the configuration information is stored directly on the disk itself, from where it is read into the registry when the multidisk is first mounted, thanks to which, on the one hand, Microsoft was able to avoid rewriting the old (and already debugged) code, and on the other hand, when the registry is destroyed, the system is reinstalled, or a disk (array of disks) is connected to another system, they are automatically mounted.
For marketing reasons, the cartoons were renamed dynamic disks (dynamic disk) and Microsoft launched a whole marketing campaign to promote them to the market. Moreover, if when updating NT 4.0 to W2K, information about existing multi-disks was normally read from the registry, then XP does not see them point-blank, and therefore an attempt to upgrade NT 4.0, which works with multi-disks, to XP or Server 2003/2008, leads to an irreversible loss data that must first be copied to another medium.
In W2K+, information about dynamic disks is stored on the disks themselves in structures PRIVHEAD and LDM .
A dynamic disk is an ordinary software RAID, of which there are dozens of implementations. Microsoft promotes not the best and, moreover, far from a free solution, bombarding consumers with abstruse terminology and trademarks.
Six reasons against dynamic disks
First. Converting a basic disk to a dynamic one is an almost irreversible operation (the exception is Simple partitions, which can be turned into ordinary volumes by editing the disk at the sector level, see "Aircraft or make a normal disk out of a dynamic disk", but composite, striped, and even more so RAID-5 disks can only be converted back by copying data to external media, deleting dynamic disks, and then creating regular partitions).
Second. Having converted the system disk to dynamic, we will no longer be able to update or reinstall Windows, since the dynamic disk installer, alas, does not understand and is unlikely to understand in the future (Server 2008 beta 3 still does not support such an operation).
Third. Linux and xBSD do not natively support dynamic disks and require the installation of third-party software (for example, "Paragon LDM/NTFS driver" - http://paragon-software.com/) to work with them, but this is not so bad. Some types of dynamic disks are supported only by "advanced" versions of Windows, and therefore, when upgrading from Windows XP Home to Windows Vista Home Base/Premium, we will be surprised to find that dynamic disks are "missing". And all because Microsoft really wants money.
Fourth. In case of serious damage to a disk volume, restoring data on dynamic disks is much more difficult than on conventional disks and at least an order of magnitude more expensive. Hackers only gutted the format that describes the structure of dynamic disks, but there are still many white spots and there are no really effective utilities for automated recovery today.
Fifth. Dynamic disks have problems with the Cluster Service and Shadow copy, and in order not to mess up, you need to light up the Knowledge Base, and then, I apologize for the expression, put on a condom and have sex.
Sixth. "Serious" servers are traditionally equipped with hardware RAID controllers, while "non-serious" servers generally don't need dynamic disks and they cause more problems than they solve.
Aerobatics or we make a regular one from a dynamic disk
A simple volume obtained by upgrading a basic disk to a dynamic one can be reverted back by running the disk editor and changing the partition type from 42h to 07h. After the reboot, Disk Manager will lose the dynamic disk, marking it with a red cross, but this is not a problem - and it can be safely deleted. But the restored basic disk is recommended to be processed with the chkdsk utility.
On Linux, you can do without a special partition editor.
The first 446 bytes on the disk are the bootloader code, followed by descriptions of the four main sections, 16 bytes each. The section type code is the fifth byte in the description. ()
That is, to convert a dynamic disk to a basic one, you need to write bytes to the disk 07h with an offset of 450.
printf "\x07" | dd of=/dev/sdx bs=1 count=1 seek=450
/dev/sdx- our dynamic disk.
The original source, i.e. Microsoft tech support, claims the following about dynamic volumes.
Dynamic storage is supported in Windows 2000 and Windows XP Professional. A disk initialized for dynamic storage is called dynamic. A dynamic disk contains dynamic volumes, such as simple volumes, spanned volumes, striped volumes, mirrored volumes, and RAID-5 volumes.
Translated into Russian, it sounds like this: dynamic disks are needed only for RAID. Converting a disk from basic to dynamic is preparing it for participation in a RAID array.
Naturally, we are talking only about software RAID implemented by means of Windows OS.
AT striped volume data is distributed serially and evenly across multiple physical disks. A striped volume cannot be mirrored, expandable, or fail-safe. Another name for such volumes is RAID-0.
I'll open the scary. Despite the impotence of software RAID in Windows, in general striped volumes (RAID-0) can be mirrored.
Although I agree, the perversion is terrible.
On the other hand, Microsoft is not shy about the quality of its technical support.
MICROSOFT AND/OR ITS SUPPLIERS MAKE NO REPRESENTATIONS ABOUT THE SUITABILITY FOR ANY PURPOSE OF THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THE DOCUMENTS AND THE RELATED GRAPHICS POSTED ON THIS SERVER. ALL OF THESE DOCUMENTS AND GRAPHICS ARE PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND.
Terms of use documentation, black on white.
Total
- When creating dynamic volumes in Windows, a different, non-classic disk partitioning scheme is used
They came up with their own marking scheme. Here, as elsewhere, microsoft is ahead of the rest and does not use generally accepted standards. - You can restore, view, transfer information only using professional and server modifications of Windows.
- Never use dynamic disks and volumes for data storage.
At one time, the creators of the Windows NT 5.0 operating system (which revealed itself to the world on February 17, 2000) brought with it many new interesting features compared to its predecessors.
One of the most noteworthy innovations in Windows 2000 was dynamic disks, the exact opposite of the old basic (or "basic") disks, which were standard disk drives and first appeared in MS-DOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System). Any main drive has the corresponding structure:
- System partition(sometimes referred to as "primary") is a partition that contains the base operating system files (such as Windows files). As a rule, the system partition is indicated by the letter "C".
- Additional section- this is a section that stores the user's personal data (for example, photos, songs, videos).
- logical drive- this is part of an additional partition that performs the same functions as the system partition. The only difference between this disk and the system partition is the inability to run an operating system on it.
Dynamic disks, in turn, support the concept of volumes, which are units of storage, using unused areas of the hard disk.
Any dynamic disk volume can have the following structure:
- simple volume- analogue of a regular partition in basic disks. It is located on only one hard drive. Has an average performance.
- Composite volume- many simple volumes combined into one large volume. Unlike a simple volume, it can be placed on multiple hard drives at the same time. This implies an important drawback of a spanned volume - a high risk of information loss if one of the hard drives is faulty.
- Mirror volume- this is a set of volumes that ensure the safety of data due to their duplication. All data contained on the first disk is copied to the second. Therefore, if one of the disks fails, the duplicated information will be available on the other disk. A mirrored volume is a good example of reliability, but it makes up for it in poor performance due to copying data to a mirrored disk.
- Striped Volume- an analogue of a spanned volume (must have at least two disks), but differs from it in that the information is distributed evenly across all disks that are part of a striped volume. A hard drive failure can cause complete data loss without the possibility of recovery. In compensation, a striped volume provides a high speed of writing data to disk.
Basic to Dynamic
To make the primary disk dynamic, you need:
- Select the "Disk Management" option (it's in Control panels, then go to the "Administration" section, and then - "Computer Management").
- Using the Run tool (Win + R) and entering the command diskmgmt.msc
A small window will appear on the screen with the appropriate name.
- In the menu on the left, the user must select the "Disk Management" section. Further conversion is carried out by pressing the right mouse button, for example, on the first disk and selecting the command "Convert to dynamic disk ..."
- At the same time, a warning will appear that after this procedure, the user will not be able to install Windows on this disk (there will be no option to select a converted disk in the Windows installation menu).
And back
It is worth noting that the user can make a dynamic disk basic, but this process will take a little longer.
In addition, before this copy all information from a dynamic disk to another media.
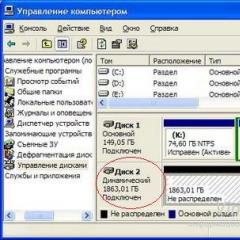
- Without leaving the "Computer Management" window, you need to define a dynamic disk (it differs from the base one by a shaded field).
- Next, in the "Action" menu, select "All Tasks", and then click on "Delete Volume".
- A window will appear informing you that all data will be lost if this operation is performed. We agree.
- Now the inscription (under "Disk [number]" in the light gray block on the left) about the current status of the disk will change from "Healthy" to "Unallocated".
- Then, by right-clicking on the light gray (pale) block, we call up the context menu and select the option "Convert to basic disk ..."
- The caption under "Disk [number]" will change to "Basic".
- With the white block of this drive selected, launch the Partition Wizard (“Action”, “All Tasks”, “Create Partition…”)
- In the wizard window, first select the type of partition, set its size (or accept the value suggested by the computer), select the letter that our disk will be designated with (or accept the one suggested by the computer), the cluster size and check the box next to "Quick format".
- Click on "Finish".
And create a logical impossible to create a partition.
This is especially true when installing a new disk, and partitioning an existing one.
Let's start with some theory:
Base or basic A basic disk is a physical disk that contains basic volumes: primary partitions, extended partitions, and logical disks. Basic disks are used, for example, on laptops or in situations where you want to install multiple operating systems on different partitions of the same physical disk.
Dynamic disk (dynamic volume; dynamic disk, dynamic volume) is a physical disk available only for Windows 2000/XP/Vista/7/8. They provide features not supported by basic disks, such as support for volumes spanning multiple disks. Dynamic disks use a hidden database to keep track of information about dynamic volumes on a disk and other dynamic disks on a PC. When you convert a basic disk to dynamic, all existing basic volumes become dynamic. You can expand dynamic volumes or create mirrored dynamic volumes, and add new dynamic disks without restarting your PC.
Now let's move on to practice.
Create a dynamic disk from a basic disk.
1) Right click on the icon my computer and select from the context menu Disk Management(suitable for all OS versions (In Windosw 7 item Control)).
2)
Go to tab Disk Management and select the white field - dynamic disk
3)
Menu Action –> All tasks –> Delete volume...(or right-click the hatched RMB field and from the context menu select Delete volume...).
4) A window will appear with the message “ All data on this volume will be lost. Do you want to continue?» Click Yes.
5)
The color of the header of the shaded field will change to black (and the text will become not allocated).

6) Right-click on the light gray rectangle to the left of the shaded field (where the inscription Disk… Dynamic…GB Connected) as above.
7)
From the context menu select Convert to Basic Disk(or select a light gray LMB rectangle and select the menu Action –> All tasks –> Convert to Basic Disk). At the same time, the inscription Dynamic will change to Basic.

8) Select the white field of the disk, then the menu Action –> All tasks –> Create section...(or click on the hatched RMB field and select from the context menu Create section...).
9)
run Partition Wizard

10) In the first window, click Further;
– select the partition to be created (primary or secondary) –> Further;
– set the size of the partition (or choose the one offered by the system) –> Further;
- assign a drive letter (or select the one offered by the system) -\u003e Further;
- specify the cluster size (or by default), set the volume label, check the box Quick Format –> Further –> Ready.
A dynamic disk is an ordinary physical disk, but with a certain set of specific functions. As a rule, these functions are not supported by basic Windows disks, but they have one useful property - they allow you to combine several disparate physical disks into one logical volume.
A dynamic hard disk, to maintain its performance, uses a hidden database that keeps track of changes to all information located on physical disks. This technology is widely used in computers that run under the operating systems of the Microsoft family. It was first implemented back in 1999 on the Windows 2000 operating system. Now all operating systems of the Microsoft family have this function.
Today, it is not difficult to convert a hard disk to a dynamic disk. To do this, the operating system has a special utility.

As a result of converting the main disk, all basic volumes that already exist on the computer are also changed. A dynamic disk has one big advantage - it allows you to literally change the size as you like on the go. This is a rather useful feature that allows you to increase the volume of one of the logical disks at the necessary moment by reducing the volume of the other.

Another indisputable advantage that a dynamic disk has is an unlimited number of logical volumes. This property will be appreciated by those users who love the order and clear distribution of information available on the computer. Thanks to this, the limitation of a physical hard disk to create no more than four logical volumes is overcome. In addition, a dynamic disk can be easily transferred to any other computer.
Despite all the advantages, dynamic disks have a number of unpleasant limitations and disadvantages:
First, they cannot be used when building cluster systems.
Secondly, the transfer of a dynamic disk to a basic one takes place only with the loss of a certain
Thirdly, a completely logical restriction on including the impossibility to put more than one given type. This greatly complicates the work of professionals who work simultaneously in different information processing environments.
Previously, there was also another limitation - dynamic disks did not work on laptops. To date, this problem has been solved, which makes it possible to use the capabilities of computing machines to the maximum.
Dynamic disk is convenient and easy. But it is always worth remembering the disadvantages mentioned, otherwise you risk important data stored on your hard drive. Remember: it is better to initially weigh all the pros and cons, and then choose the best option for yourself. It is always easier to prevent a problem than to solve it.