Vmware won't start virtual machine after reboot. Guest OS does not start in VMware Workstations. Opening a virtual machine
Read how to restore a deleted VMware Workstation virtual machine or the contents of a virtual machine disk. Which built-in virtual machine tools or third-party programs to use to restore it. and VMware Player is a virtualization software that is designed to run multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single physical computer.
VMware is one of the most stable and secure computer virtualization platforms that allows a large number of IT professionals, developers and other company professionals to be more flexible and productive in their work.
Content:VMware Workstation System Files
That is, VMware Workstation is another virtual running operating system inside your computer's operating system. All files of this operating system (both system and user's personal files) are stored on the computer's hard drive, and by default they are located in the folder:
C:\Users\ Username\Documents\Virtual Machines\ Name of the virtual machine
Most often, users do not need to know the name and location of the VMware virtual machine files. The program itself manages its files. But there are situations when such knowledge is indispensable, for example: if a virtual machine needs to be restored in case it is lost, or if deleted files are recovered from it, etc.
As you can see from the screenshot above, the virtual machine folder consists of a certain set of files. VMware creates such a separate folder for each virtual machine and names it with the name of the virtual machine, which is assigned by the user during the installation of the virtual operating system.
The main files of the virtual machine have the following extensions:
- *.log– VMware Workstation key activity log file. It is used for troubleshooting, should they occur.
- *.nvram– file of the status and BIOS settings of the virtual machine
- *.vmdk– a virtual disk file that stores the contents of the virtual machine's hard disk
Note. Depending on the settings of VMware Workstation, the virtual machine disk may consist of one or more *.vmdk files. - *.vmem- paging file of the virtual machine. Created and visible only while the virtual machine is running
- *.vmsd– current snapshot parameters file
- *.vmsn- a snapshot state file that stores the current state of the virtual machine while it is being used
- *.vmss– state file of the suspended virtual machine
- *.vmtm– configuration file, one of the virtual machine parameter files
- *.vmx- the main configuration file, which stores all the parameters of the virtual machine
- *.vmxf– additional configuration file.
Note. Files with the described extensions are the main ones. The virtual machine folder may also contain other files and folders, including those that are displayed only while it is running.
How to restore a virtual machine that has been deleted
Accidental deletion, formatting the computer's hard drive, or corrupting the file system can all cause data loss. But, as a rule, virtualization software does not provide built-in recovery features. In this regard, the issue of restoring virtual machine data becomes a rather difficult problem for users.
The previous paragraph of the article describes the main types of files that make up a virtual machine and in which all its data is stored. After restoring them and opening the main configuration file in VMware, which stores all the parameters of the virtual machine, the user has the opportunity to restore the lost virtual machine.

To restore a virtual machine that has been deleted:

How to restore the contents of a VMware virtual machine disk
As we have already discussed, all files that are saved on the disks of a virtual machine are located in the .vmdk files of the virtual disk. Hetman Partition Recovery hard disk data recovery program has the function of mounting virtual disks and recovering data from them.

If for some reason your virtual machine has lost its functionality, and important files were stored on its disks, you can restore them. For this:

How to recover a VMware virtual machine disk file from the virtual machine itself
As a result of the experiments, it was found that files that are deleted or lost inside the virtual machine cannot be recovered.

Although VMware Workstation is a virtual machine, quite real data can be stored on it. In this regard, the loss of access to a virtual machine or its removal can be an unpleasant surprise, and the ability to restore will save user data from possible irretrievable loss.
Vmware virtualization products make it easy to run any operating system for testing or run any application. This can be useful if you want to test your application before production, check service packs or hotfixes, or run a legacy application. Whatever the reason, Vmware offers several virtualization applications: VMware Player,
VMware Server, and VMware Workstation. The first two products are free, the last is paid, but has a large number of features.
After installation, Vmware products, unlike Microsoft products such as Virtual PC 2007 or Virtual Server 2005, install services on the computer that are configured to start automatically when the computer boots. You may not be using virtual machines all the time, and you don't want Vmware services to be running all the time and using system resources. These services can sometimes even slow down system boot times.
This lists all the services that automatically start when Windows boots.
- VMware Agent Service
- VMware Authorization Service
- VMware DHCP Service
- VMware NAT Service
- VMware Virtual Mount Manager Extended
The simplest solution is to set these services to manual boot mode so that they do not start at system startup. Follow these steps:
You can also automate these actions by running the following commands:
Sc config VMAuthdService start= demand sc config VMnetDHCP start= demand sc config "VMWare NAT Service" start= demand sc config vmount2 start= demand
You can create a text file with the commands above and save it as a batch file, for example Set_VMware_services.bat.
Next, instead of manually starting and stopping services every time you want to start VMware Workstation, create 2 batch files. One will be used to start all services when required, the second to stop.
Copy the following lines to a text file and save it.
Sc start VMAuthdService sc start VMnetDHCP sc start "VMWare NAT Service" sc start vmount2 "C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Workstation\vmware.exe"
By the way, you can use the NET START command instead of using SC.
Note: Change path from C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Workstation\ on the C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Server\ if you are using VMware Server.
Whenever you want to start VMware Workstation just run the file VMware_Workstation_Start.bat.
Copy the following lines to a text file and save it:
sc stop VMAuthdService sc stop VMnetDHCP sc stop "VMWare NAT Service" sc stop vmount2
When you want to end using VMware Workstation just run the file VMware_Workstation_Stop.bat to stop VMware services.
guard
Do you know what is? I do not know either. But Andrei Belyaev in the sports library may know
Many users of the VMware Workstation desktop platform and the VMware Server server platform would like to have their virtual machines automatically start when Windows starts but before they log in. This is necessary so that in the event of a computer restart, the virtual machines would automatically “raise”, and administrator intervention would not be required.
To implement this, you will need to configure the virtual machine to run as a service. So, to get started you will need:
- Utility Instsrv.exe.
- Utility Srvany.exe.
All this can be obtained in a package (rktools.exe) downloaded from the Microsoft website.
Install this package and then copy instsrv.exe and srvany.exe to catalog windows\system32. After that, you need to restart your computer.
Now locate the VMware Workstation or Server executable (for example, c:\program files\vmware\vmware workstation\vmware.exe) and the main configuration file of the virtual machine (for example, C:\mymachines\WinXp\winxp.vmx).
Instsrv vmware_winxp C:\windows\system32\srvany.exe, where vmware_winxp is the name of your new service.
After that, go to the registry editor (regedit.exe) and find this key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\vmware_winxp
Create a new key Parameters(to do this, right-click on the service name, then New->Key).
Create a new type value string value in key Parameters, as it shown on the picture:
We name the value Application.
Double click on the value and in the field value data write the path to VMware Workstation, the virtual machine startup key and the path to the virtual machine vmx file (do not forget the quotes):
"C:\program files\vmware\VMware Workstation\VMware.exe" –x "C:\mymachines\WinXp\winxp.vmx"
Now that you've created the service, you need to configure the startup options for it. To do this, run Start->Run and write services.msc.
You will see a list of available services. Find the vmware_winxp service you created and double click on it. The service properties appear. Set on tab General startup type Automatic, go to the tab log on. Here set the parameter Log on as meaning Local System account and be sure to check the box Allow service to interact with desktop.
Now you can test the autostart of the virtual machine by selecting the item from the context menu of the service Run. When starting a virtual machine, a request to change the unique identifier (UUID) may pop up, you must select select the item Create. In addition, you need to make sure that all unnecessary devices for the virtual machine are disabled (Virtual CD-ROM, floppy). Also add the following line to the vmx file to disable tooltips:
Hints.hideall="TRUE"
Now that's it - restart your computer and test autostart of the virtual machine as a service.
Vmware Workstation is the software that is most often used to create virtual machines with various operating systems. The possibilities of this program are quite large.
Today we will consider the process of creating a virtual machine with the Windows operating system. A big plus of the Vmware Workstation program is the ability to run and work simultaneously with several virtual machines. The number of simultaneously running virtual machines is limited only by the hardware component of your computer and the settings for allocating computer resources for the operation of these machines.
The program itself is not demanding on the hardware of your computer. A 2-core processor and 2 GB of RAM will be enough for you, but if you are going to work with several virtual machines at the same time, you should think about improving these parameters.
Download and Install Vmware Workstation
First we need to download and install the software.
You can download from the official site https://www.vmware.com/products/workstation-pro/workstation-pro-evaluation.html
When you go to the download page, you can choose for which operating system you will use this software.
After downloading, install. 
After installation, run the program. 
Now we can start installing and configuring our virtual machine.
Create and configure a virtual machine
First, we need to prepare an image of the desired operating system that we want to install.
To create a virtual machine, click on the "File" menu button and select "New virtual machine ...". 
This will open the window for creating and configuring a new virtual machine. In the window that opens, select "Custom (Advanced)" and click the "Next >" button. 
The next window prompts you to select a version for hardware compatibility. This is necessary for the installation of lengthy tools and programs, and the selection of the necessary parameters. We do not need this, so we do not select anything and click the "Next" button. 
The next step is to select the source (image) of our operating system.
If you want to install the operating system from a disk that you have, in this case, select the "Installation disk" item.
In the event that you have an image of the operating system, then select the item "Installation Image File" and press the "Browse" button. In the window that opens, select the image you need and click the "Open" button. The image file must have an .iso extension. In our example, we will install Windows XP.
To install Windows 7/8/8.1/10 operating systems, you need to activate the hardware virtualization option (Virtualization Technology) in the BIOS. This option is available for AMD and Intel based computers. Without the activation of this technology, these operating systems will not be launched.
After choosing the method we need, click the "Next" button. 
If you know the product key, then enter it in the window that opens in the line "Windows Product Key", if you don't know it, then just fill in the fields we need (If you don't need a password, just leave this field blank). After filling in the required fields, click the "Next" button.
If the product key has not been entered, then during the simple installation process, the system itself will ask you to enter it. 
In the next window, we set the name of our virtual machine, which will be displayed in the list of virtual machines. And select the directory where the files of the virtual machine will be located.
After the done actions, we proceed to the next step. 
The next window will be "Processor Configuration".
Here you can select the desired parameters of your processor resources that the running virtual machine will use.
By default, the program automatically selects the optimal processor parameters, but if they do not meet your requirements, you can determine them yourself by selecting the desired configuration manually.
After determining the necessary parameters, proceed to the next step, click the "Next" button.
It is worth noting that the more resources you give to a virtual machine, the less of them will be left for each virtual machine or your operating system to work during its active operation.
In the Network Type window, you can configure the network settings for your virtual machine.
The Vmware Workstatio program allows you to fine-tune network access for a virtual machine.
- If you want to provide access to your machine from the Internet, you should select the First item "Use Network Bridge". When using this option, you will need to set an external (whitelisted) IP address for your virtual machine.
- In order to use a virtual machine inside the network and provide it with access to the Internet, you must select the second item "Use network address translation (NAT)".
- In the event that you want to restrict access to the Internet and use the virtual machine purely on the internal network, you should select the third option "Use host network only".
- And the last option is to refuse to use a network connection, when you select this item, your virtual machine will not have access to any network.
We need to choose the second option, for normal work. After selecting the desired option, proceed to the next step. 
In the window for selecting the type of controllers, select the driver for the SCSI controller.
To configure these parameters, you must first activate support for SCIS controllers in the BIOS, if it is not activated.
We will be given 3 types of drivers to choose from:
- Bus Logic
- LSI Logic
- LSI Logic SAS
If you have knowledge of these drivers, then you should choose the one that your operating system supports. In the event that you are not familiar with them, then we simply do nothing, the Vmware Workstatio program automatically selects the controller driver that suits your operating system.
After selecting the driver, proceed to the next step. 
In the next window, you need to select the type of virtual disk.
The system will automatically determine the type of disk that is suitable for your virtual machine and its operating system, but I recommend choosing SATA, since this type of disk is currently the fastest in comparison with others.
It is worth noting that some types of operating systems (rather old ones) will not be able to work on a SATA type disk, in which case you should choose another type of virtual disk that suits your OS, or simply trust the program, as it will automatically determine the correct type.
After selecting the desired type, proceed to the next step. 
In this window, we will be able to choose which disk to use to install our virtual machine.
- Create a new virtual disk - when choosing this option, you can specify the folder and its size where the operating system of your virtual machine will be installed.
- Use an existing virtual disk - if you have previously created a virtual machine and want to repeat its virtual disk settings or simply reinstall, then you can select this option and specify the folder of your old virtual machine.
- Use Physical Disk - Select this option if you want to use a separate local hard disk for your virtual machine.
In our case, we choose the first option and move on to the next step. 
In the next window, you must specify the size of the virtual hard disk.
The program will automatically indicate the appropriate size for your type of operating system, but if you need more or less, then indicate the size we need in the "Maximum disk size" field.
Keep in mind that the amount of free space on your disk will decrease exactly by the amount that you specify to reserve for a virtual machine. Make sure that you have enough free space for comfortable work with programs and for the correct operation of the operating system.
After determining the size, proceed to the next step. 
Specifying a wild file. We choose where the file of our virtual disk for the virtual machine will be located. Press the "Browse ..." key and specify the folder or create it. 
We have now moved on to the final step of setting up our virtual machine and its operating system.
In this window, we can once again view the list of all the parameters we have selected and, if corrected, use the "Hardware settings ..." button.
In the "Hardware settings ..." section, you can fine-tune the hardware settings for your virtual machine or, if necessary, change the previously set ones.
After installation, the system will start by itself.
Now we have a virtual machine to work with the Windows XP operating system. You can install other versions of Windows in the same way.
You can observe and launch all installed virtual machines on the left side of the program under the names that you set them during installation. 
To go to the settings of an already installed virtual machine and its operating system Right-click on the virtual machine and select "Settings ..." from the drop-down menu.
This will open the options window. 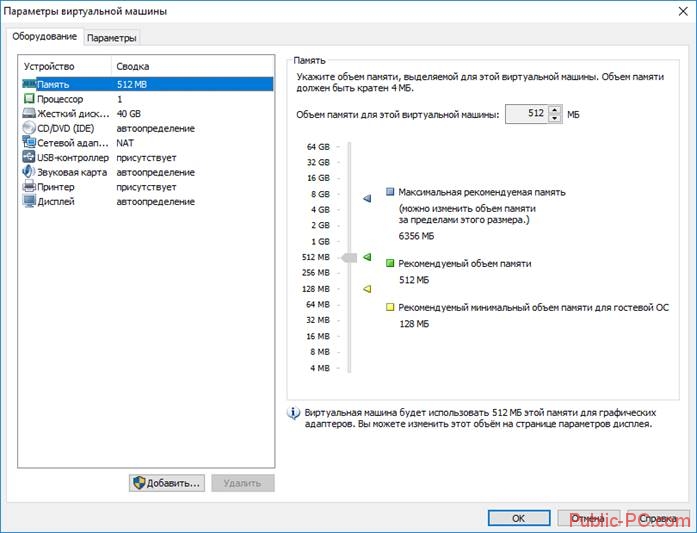
Deleting a virtual machine
First of all, for that. To delete a virtual machine, you need to end the guest session.
To do this, right-click on the virtual machine, and in the drop-down menu, hover over the "Power" item, then select "Shut down the guest OS" in the drop-down menu. The OS will shut down, after which we again right-click on the virtual machine and select the "Delete" item, we agree with all pop-up windows.
Thus, you have completely deleted the virtual machine and all its files from your computer.
Problems starting a virtual machine
In the event that your virtual machine does not start, you should do the following steps.
- Checking BIOS settings (activating virtualization technology and SCSI controller support)
- Reinstalling the operating system.
- Installing the system from another image or disk.
- Checking the virtual machine settings (perhaps some settings are not compatible with your OS).
- Checking hard disk integrity.
- Diagnostics of the computer on the workload of the operating system.
- Disable Firewall.
- Malware check.
If none of the methods helped you, then you should carefully read the error that appears when you start the machine and understand what the problem is. After you understand what the problem is, you can solve it by following the instructions described in the error.
Conclusion
Following the instructions described in the article, you can easily install, configure and run your virtual machine with the desired operating system.
The main thing during installation is to clearly follow the instructions in order to avoid errors when starting and running the virtual machine in the future.
Also, do not forget to make preliminary settings in the BIOS for the correct operation of the Vmware Workstation program.
VMware Workstation is a virtual machine for running operating systems installed on a computer. VMware virtual machine emulates computer hardware, allows you to create virtual machines, run one or more operating systems running in parallel with Windows installed on the computer.
The VMware Workstation Pro program emulates the hardware of a computer and allows you to run software on the computer in an isolated environment. You can install operating systems (for example, Linux on Windows, or vice versa) on a virtual machine to work in a virtual environment without affecting the real system.
Check for unfamiliar or suspicious software, test a new antivirus without installing it on your computer, try a different operating system, etc. In this case, the real operating system will not be affected in case of dangerous actions performed on the virtual machine.
The actual operating system installed on the computer is called the host, and the operating system installed on the virtual machine is called the guest operating system.
The American company Vmware, the largest manufacturer of software for virtualization, produces programs for personal computers: paid VMware Workstation Pro and free VMware Player with reduced capabilities.
VMware Workstation Pro (in the article an overview of this program) supports the installation of several different (or identical) operating systems: various distributions of Windows, Linux, BSD, etc.
Note that the guest operating system consumes computer resources. Therefore, while the virtual machine is running, resource-intensive applications should not be launched on a real computer, and several virtual machines should not be opened at the same time. The more powerful the computer, the more comfortable it is to work on a virtual machine. On powerful computers, several virtual machines will work without problems at the same time, and on weak computers, only one virtual machine.
Install VMware Workstation Pro on your computer. By default, the program works in English, on the Internet there is a good Russification from Loginvovchyk, which must be installed after installing the program. After that, the VMware Workstation Pro virtual machine will work in Russian.
Once launched, the main VMware Workstation window will open. At the top of the window there is a menu for managing the program. On the left is the "Library", which will display the virtual machines installed in VMware. The "Home" tab contains buttons for performing the most frequently requested actions: "Create a new virtual machine", "Open a virtual machine", "Connect to a remote server", "Connect to Vmware vCloud Air".

Create a new virtual machine
To create a virtual machine (VM), click on the "Create a new virtual machine" button, or enter the "File" menu, select "New virtual machine ...".
The New Virtual Machine Wizard opens. In the first window, select the "Normal (recommended)" configuration type, and then click on the "Next" button.

The next window prompts you to select the type of installation of the guest OS, three options are available:
- installation from an installation DVD inserted into the computer's drive
- use to install an ISO system image file from a computer
- installing the operating system later
If you select the first two options, after selecting the settings, the installation of the operating system on the virtual machine will begin. In the third case, the installation of the guest OS can be started at any other convenient time, after the virtual machine is configured.

If installing later, select the guest operating system. If it is not in the list, select "Other". Then select the OS version. There is a large selection of versions for each system (more than 200 operating systems are supported in total), there is also an Other variant of various bit depths (34-bit and 64-bit).

If you are installing a guest system during the creation of a virtual machine, then a window with information about the quick installation will open. The Windows product key and password are optional, you only need to select the Windows version.

If your computer has more than one logical disk, then I recommend changing the location of the virtual machine's files in the user profile (default setting) to a different disk on your computer.
What is it for? If the Windows installed on the computer fails, you will need to reinstall the system. After reinstalling the operating system, the VMware virtual machine file stored in the user profile on the system drive will be lost. If the virtual machine is not located on the system drive, then reinstalling Windows will not affect it.
For reuse, you will need to install the VMware Workstation program, and then connect the virtual machine. No need to reinstall and configure everything.
Therefore, on the “E” drive (in your case, it will most likely be the “D” drive) of my computer, I created the “Virtual Machines” folder, in which the folders with the files of the virtual machines installed on my computer are saved.
For a new virtual machine, create a folder with the name of this VM in order to separate its files from other VMs.

Next, you need to select the maximum size of the disk occupied by the virtual machine (by default - 60 GB, the size can be changed), the type of virtual disk saving: in one file, or in several files. This size will be taken from your computer's hard drive for the needs of the virtual machine.
When saving a virtual disk in a single file, the VM performs better than when it is divided into several files.

In the final window, click on the "Finish" button. After that, the installation of the guest operating system will begin.
If the setting was selected to install the operating system later, then in this window there will be no item “Turn on this virtual machine after its creation”, respectively, the installation of the guest system will not start.

Setting up a VMware virtual machine
By default, the virtual machine setup is optimal for most cases. If necessary, you can change some settings, as well as add shared folders.
In the settings, in the "Hardware" tab, you can change the amount of memory for this virtual machine, the number of processor cores, and the amount of hard disk occupied by the virtual machine. In the "CD / DVD (SATA)" section, you can select a drive or operating system image file for installation (if you choose to install later), make other settings.

In the "Options" tab, in the "Shared Folders" section, select the "Always On" setting, activate the "Mount as a network drive in guest Windows" item.
Next, click on the "Add ..." button, in the Add Shared Folders Wizard window, create a shared folder for exchanging data with the real system and other guest systems. It is desirable to create a shared folder not on the system drive for the reasons described above.
There is already such a folder on my computer (Data Sharing). I chose this folder for the new virtual machine. Next, enable this resource.

The default settings allow dragging, pasting and copying files from the real to the virtual system and vice versa.
Opening a virtual machine
After reinstalling Windows (my case), you can open previously created virtual machines saved on your computer. In the main window of VMware Workstation, click on the "Open virtual machine" button, or select "Open ..." from the "File" menu.
Select the file (on my computer the virtual machines are located in the "Virtual Machines" folder) of the virtual machine, and then click on the "Open" button.
On my computer, I opened previously saved virtual operating systems: Windows 10 x64, Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7, Mac OS X.

Running a Guest OS in VMware Workstation
To start a guest operating system, in the VMware Workstation Pro program window, select the tab with the required OS (if several guest OSes are installed), and then click the "Turn on the virtual machine" button. You can turn on the system from the menu "Virtual machine", "Power", "Start virtual machine".
Installing VMware Tools
VMware Tools is a package of drivers and services that improve the operation of a virtual machine and its interaction with peripheral devices. Immediately after installing the operating system on the virtual machine, you need to install VMware Tools. A reminder of this will appear in the program window.
From the "Virtual Machine" menu, select "Install VMware Tools Package...". Next, open File Explorer, run the VMware Tools installation from the CD-ROM drive. After the package installation is complete, reboot the guest operating system.
Guest OS Snapshots
In VMware Workstation, you can take a snapshot of the state of the guest OS. After creating a snapshot of the system state, in case of failures in the guest OS, you can return to the previous working state of the system.
In the "Virtual Machine" menu, you need to click on the item "Create snapshot". Next, give the snapshot a name, if necessary, add a description.
To restore the state of the guest OS at the time the snapshot was taken, select Revert to Snapshot: Snapshot N from the context menu. Next, restore the system state. The current state of the OS will be lost.
Created snapshots can be managed through the Snapshot Manager: create, clone, delete snapshots. There are three buttons on the menu bar for managing system snapshots.
Shutting down a virtual machine
To exit the virtual machine, in the "Virtual Machine" menu, click on the "Power" context menu item, and then select "Shut down guest OS". The operating system will shut down as if it were a normal shutdown of the computer.
When you select the "Suspend guest OS" option, the system will suspend its work, without disabling services and applications.
Deleting a virtual machine
To delete a virtual machine, open the virtual machine's tab in VMware Workstation Pro. In the "Virtual Machine" menu, select the "Manage" context menu item, and then the "Delete from disk" item. In the warning window, agree to the deletion (this is an irreversible action).
After that, all files of the guest virtual machine will be deleted from the computer.
Conclusion
VMware Workstation Pro Virtual Machine is a powerful application for creating guest virtual operating systems that run on a computer along with the real OS. The guest operating system will be isolated from the Windows installed on the computer.