Install a local server on the computer. How to create, install, configure a local server on a computer What does a local computer mean
In today's world, LANs have become more than just a necessity - they're actually required to achieve a good level of productivity. However, before you start using such a network, you should create and configure it. Both of these processes are quite difficult and require maximum concentration, especially the first of them. A poorly designed and configured LAN will not work at all, or it will not function at all as it should, so creating a local network should be the focus of attention for the person doing it.
What is a local network
As a rule, the creation of such communication systems is caused by the need to share data by users who work on remote computers. A LAN not only enables near-instantaneous exchange of information and simultaneous file sharing, but also allows remote use of network printers and other devices.
A local network is a complete set of software and hardware resources aimed at creating a single information space. In fact, this is a number of computers located at a distance from each other and connected by a communication line - a cable. The main difference between a LAN and other types of networks is the short distance at which workstations are located.
Pre-project preparation and design
Before you create a local network, you must first design it, that is, plan the process of its creation. This stage is one of the most significant, since the LAN includes a huge number of components and nodes.
Initially, the terms of reference are drawn up on the basis of primary data, defining several points:
- Functions and tasks of the LAN.
- Selected topology.
- List of available equipment.
Once you have these points in mind, you can start designing. The project itself should contain LAN schemes, network equipment placement points, a list of required software and hardware.

A local area network is a complex mechanism, but if it is designed correctly and the equipment is selected in accordance with the requirements, then the likelihood of problems in the operation of the communication mechanism becomes minimal.
Required Hardware
There is a list of equipment without which no LAN can function. It includes:
- Data lines. The most commonly used coaxial cable and optical fiber. In this case, the length of the coaxial cannot exceed several hundred meters, however, if it is necessary to extend the network over long distances, special repeaters are used - signal repeaters that do not allow it to fade.
- Communication equipment: network cards (devices that perform duplex exchange of information between a computer and a data transmission medium), hubs (break the network into separate segments, structuring the network physically), routers (take on the choice of the packet transmission route), switches (logically divide the LAN into segments, combining several physical circuits), repeaters (provide signal recovery, allowing you to increase the length of the transmission medium), transceivers (amplify the signal and convert it to other forms, allowing you to use different data transmission media).
List of software
No LAN is complete without software. Required LAN programs include:
- Operating systems of work nodes. The most commonly used operating system remains Windows 7, although Windows XP is also not losing ground.
- Network operating systems installed on servers are the basis of the LAN, since it is impossible to set up a local network without them. Exactly these software take control of all data flows between the main and secondary nodes, providing the possibility of collective access to network resources. As a rule, the following Microsoft operating systems are used: Windows Server 2003 or 2008.

- Network services and applications that allow users to access remote files, print documents to a network printer, view networked work sites, and send email messages. The implementation of such services is carried out using software.
Creation and installation of a LAN
Installation and commissioning work takes the most time, since it is necessary to create a local network in several stages:
- Before starting the installation of communication lines and switching devices, you must first prepare the room.
- Next, you can lay the cable, as well as install the necessary equipment.
- Devices of the server and workstations should be connected to the cable communication line.
- After that, the software is installed and configured.
Installation of cable and equipment has a number of features, therefore, if there are difficulties with how to connect a local network, better solution entrust this issue to specialists.
Joining two computers in a LAN
In some cases, it may be necessary to combine two computers into one network, for example, to create a common information space. This is not very difficult to do if you follow a certain algorithm of actions:
- If necessary, install network adapters in both computers, not forgetting the drivers.

- Purchase a crimped network cable for connection. If you have the necessary knowledge and skills, crimping can be done independently - the local network two computers from this will not become worse quality.
- Connect both workstations with a communication line.
- Set up the LAN in a specific order.
Algorithm for setting up a local network between two computers for Windows 7
- Select the "Start" menu, then, by right-clicking on the "Computer" icon, enter the "Properties" submenu.
- You need to find in the list "Computer name and domain", and then select the item with the change in settings.
- The working name of the computer must be changed by clicking on the appropriate icons.
- The group name should remain unchanged - "Workgroup", but the computer names are changed to "pc1" and "pc2" for the first and second subscriber, respectively.
- You can now click OK and restart your computer.

In most cases, you may want to give each host a unique IP address:
- From the Start menu, select Settings and then Network Connections.
- Right-click to open the "Properties" submenu next to the "Local Area Connection" icon.
- In the "General" tab, select "Properties" of the item "Internet Protocol".
- Make the line "Use the following IP address" active and enter the value 192.168.0.100. After that, save the changes made.
Local network and internet
Work nodes connected in a LAN can be connected to the Internet. A local network, to which the Internet can be connected in two ways, will work at a speed divided in two.
The first way to connect is to use a router, which is assigned an identifying IP address. And in the second case, you can use a wireless connection.
In this case, the local network is the interaction of two computers, master and slave, so the IP address is written in the gateway of the main one, previously connected to the worldwide network.

If the LAN is based on the use of a server, each workstation must have an individual IP address, and a proxy server is specified in the browser settings through which the Internet is accessed.
Wireless LAN
A wireless local area network is a type of LAN that uses high-frequency radio waves to transmit information. WLAN is an excellent alternative to the conventional cable communication system, having a number of advantages:
- Improving labor productivity. WLAN makes it possible to use the Internet without being tied to one room. You can freely change your location without losing your internet connection.
- Easy installation and configuration, financial savings and reliability - all these factors are due to the absence of a cable communication line.
- Flexibility. Installing a wireless network is real where there is no way to stretch the cable.
- Possibility of expansion. Network scalability is greatly simplified thanks to wireless network adapters, which can be installed on any worker node.
WLAN has a certain range, which depends on the characteristics of the network devices and the noise immunity of the building. As a rule, the range of radio waves reaches 160 m.
Necessary equipment for creating a wireless LAN
An access point is used to connect other workstations to the network. This device is equipped with a special antenna that controls duplex data transmission (sending and transmitting) using radio signals. Such a point can transmit a signal at a distance of up to 100 m indoors and up to 50 km in an open area.

Access points significantly expand the computing power of the entire communication system, allowing users to freely move between each of them without losing connection to the LAN or the Internet. In fact, these radio points act as hubs, providing a connection to the network.
Using access points allows you to scale up your entire wireless LAN by simply adding new devices. The number of subscribers that one radio point can withstand generally depends on the network load, since the traffic is divided equally between each of the users.
Wireless LAN: Windows 7 Setup Flow
First you need to prepare an ADSL modem with WiFi technology, as well as client points with wireless adapters connected to them. After that, you can start building a wireless LAN:
- Connect the modem to the electrical network.
- Run the WLAN setup wizard on the client device.
- Select the SSID from the list of found wireless networks.
Access point setup:
- The first step is to configure the TCP/IP protocol properties by specifying the IP address and subnet mask.
- After that, specify the value of the DNS server, since it is not possible to fully configure the local network without this parameter. In most cases, it is enough to make the automatic assignment of the DNS address active.
- It is also mandatory to configure the parameters of the wireless network itself, in which security is important.
- At this stage, you need to configure the Internet connection and filtering for the Windows 7 firewall.
- And lastly, the wires are connected and the WLAN network is tested.
To create an optimal information space, you can combine types of networks - cable and wireless, allowing you to use the advantages of each of them for the benefit of the enterprise. However, it is important to remember that in our time, it is WLANs that are increasingly being used, which have all the advantages of cable networks and are devoid of their disadvantages.
After completing the creation and configuration of the local network, it is important to provide for its administration and the possibility of maintenance. Even if the LAN is installed perfectly, during its operation various hardware or software malfunctions are almost inevitable, which is why maintenance should be regular.
Designers and administrators often need to make changes to how their site works and looks. And, as it happens, everything always works and is not displayed as planned - the background moved out, the icon is too large, errors in the scripts or database queries, in general, inadequate site operation. In such cases, you don’t want to injure the audience, no one likes to sit on an unusable project, where requests come with a delay, fatal errors. The chance of losing some of the visitors during such “experiments” is very high, not to mention the fact that there is a risk of completely breaking the structure of work and rendering the entire system unusable.
We make a local server from a regular computer
For such cases, engineering thought came up with the local placement of web servers - a completely similar technology for communicating a site with a real server, which will allow you to test all your ideas and innovations on a standalone version of your project, where your risks of data loss and other troubles.
We have dealt with a brief assignment of the local location of sites, although there are many more other reasons for this.
The software part remains - is there software that can provide us with such an opportunity? It should be easy enough to install, rich in functionality and be a complete project management tool (when managing one or more sites). Yes, there is such a product - XAMPP? to make a local server from a computer.

XAMPP - assembly with ready-made tools, supports cross-platform. Everything we need to complete the task is in it, also answering the points of multifunctionality.
Installing the program is simple and does not differ from the ordinary algorithm of pressing the “next” button, no difficult choices will be made during installation.
The interface displays all the necessary information: connected or non-functioning modules, error output / connection of certain libraries and their start / forced stop.
Directly from the program, you can launch phpMyAdmin in your default browser by starting full time job for administration - through the web interface, performing the necessary operations in MySQL, just click the Admin button.
Built-in Webalizer analyzer - site performance statistics, displayed through graphs
Mercury Mail - receiving and sending mail on a computer or to others, via a local network
FileZilla FTP - FTP server with support for drag&drop technology and directory synchronization
All of these tools give a complete simulation of a real web server, allowing you to save money - for using local hosting technology, nothing but a computer and supported operating systems not needed (xampp supports macOs and Linux), in case you decide to rent a test server for your project, which will require the same capacity payment as a regular site.
Scripting instructions in web languages like: php and JavaScript work great in the local environment as plug-ins, and directly as executable files.
The computer on which the user is logged on. In other words, it is a computer that is directly accessible to the user, that is, without communication lines and devices such as a network card or modem.
local user
The user of a computer that is not connected to the network. Usually local users called people working with a computer at home.
remote computer
A computer accessible to the user only through the use of communication lines and devices such as a network card or modem.
protocol
A set of rules for exchanging data between computers on a network, including the Internet. The protocol describes the rules for the exchange of service information, which ensures the integrity of the data.
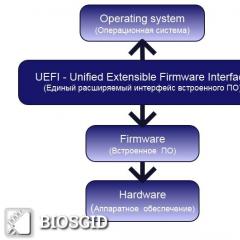
OSI reference model
A network model proposed by the International Standards Organization (ISO) to enable interoperability between vendors. OSI model- conceptual seven-level model (figure), including the following levels:
transport,
data channel,
physical levels.
applications,
representation,
Ethernet network
IEEE 802.3 standard for contention based networks. Ethernet network uses bus or star topology and CSMA/DC (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection) access control method to regulate traffic over communication lines. Network nodes are connected by coaxial or fiber optic cable or twisted pair. Data is transmitted in variable size frames containing control and address information, as well as up to 1500 bytes of data. The Ethernet standard provides data transmission without high-frequency modulation at a speed of 10 megabits (10 million bits) per second.
Wireless network
A data transmission system in which a radio channel is used as a carrier. Allows you to deploy a network where the deployment of a cable system is impossible or not economically feasible.
router
In a Windows environment, routers are devices that provide interoperability between local and wide area networks, as well as the ability to connect local networks with different topologies (such as Ethernet and Token Ring). Routers check packet headers against some local network and choose the best path for the packet, optimizing network performance.
In a Macintosh environment, routers are required to connect computers on different physical networks. Routers maintain a table of physical networks in the Macintosh internetwork and route data received from one physical network to other physical networks. The functions of routers can be performed by computers with server Windows versions and running AppleTalk network integration services. In addition, other routing equipment can be used on an AppleTalk-integrated network.
Routing
The process of forwarding packets across an internetwork from a source node to a destination node.
shared folder
A folder located on another computer that is shared over the network with other users.
shared resource
Any device, data or program shared by multiple devices or programs. In Windows, a share refers to any resource that is available to network users, such as directories, files, printers, and named pipes. The term is also used for server-based resources available to network users.
bits per second
The number of bits transmitted per second; is used as a measure of the rate at which a device, such as a modem, can transmit data.
A single set of binary data of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) network layer, consisting of the transmitted data and a header containing an identification number, source and destination addresses, and error control data.
protocol
A set of rules and conventions for transmitting data over a network. These rules define the content, format, timing, sequence, and error checking of messages exchanged between network devices.
working group
Combining computers, designed to make it easier for users to find items such as printers and shared folders. Workgroups in Windows, unlike domains, do not provide centralized account provisioning and authentication.
global networks
global network
A communications network that connects geographically dispersed computers, printers, and other devices. The WAN allows connected devices to communicate with each other. /one/
Internet
A global information network, the parts of which are logically interconnected with each other through a single address space based on the TCP / IP protocol. The Internet consists of many interconnected computer networks and provides remote access to computers, e-mail, bulletin boards, databases and discussion groups.
intranet
A distributed corporate computer network designed to provide employees with teleaccess to corporate information resources and using software products and Internet technologies. The intranet allows you to control access to corporate information.
ISP
An organization that provides Internet access to companies and individuals. The ISP provides the phone number, username, password, and other information that users need to connect their computers to the ISP's computers. As a rule, the payment for the services of the provider can be monthly or hourly.
internet server
A computer connected to a network, or a program running on it, that provides clients with access to and manages shared resources.
Each computer connected to the Internet has two equivalent unique addresses: a digital IP address and a symbolic domain address.
The most important types of servers are:
web servers;
email servers;
FTP servers for file sharing;
real-time communication servers (chats);
servers that ensure the operation of Internet telephony;
systems for broadcasting radio and video over the Internet.
A local area network is a group of computers connected together, located in a certain limited area, such as a building. The size of such a network can be different. It can include from two workstations located in the same room to several hundred workstations located on different floors of the same administrative building. In most cases, different types of cables can be used to connect computers to a single network. However, the use of wireless channels is also acceptable, which will also be discussed. So, let's understand what is a local network? It is important to note that if the network leaves the boundaries of one building, then it would be more correct to call it global. In general, from the specialized literature, it can be determined that the local network is limited by the boundaries of the building, but there are no such restrictions for the global one.
The literary definition does not always correspond to accepted standards, since usually the network is defined by functional, and not by physical features. In this sense, which is the most general, such networks are a means of communication between computers, allowing them to access different equipment. That is, such computers get access to various kinds of network resources, for example, printers, scanners, as if they were locally installed. Naturally, access to equipment also means access to data stored on this equipment.
So, in the question of what a local network is, everything may already seem clear. However, there are many nuances here. All computers in such a network are able not only to access the installed network components, but also to use them in the same way as in a local installation, which implies mandatory joint implementation of data.
The first local connected office generations - mainframes to the network, however, it was customary to install the first personal machines as separate devices. It is worth mentioning the most primitive form of a local area network, when the user copied them to a floppy disk on one device, and then switched to another to print the information or simply store it there. This decision could not be called bad, especially considering the possibility of copying large amounts of information. However, there are also shortcomings here, and very serious ones:
The risk of information loss due to loss or accidental formatting of data was very high;
Difficulties arose with the synchronization of different versions of the document, when several people had to work on it at the same time;
The size of the diskette was only 1.44 MB, and the size of the required data file could significantly exceed it;
The inability of users to work with documents when using different pre-installed applications on computers;
The data was difficult to protect, since the floppy could simply be stolen;
A significant amount of time is spent on the processes of copying files, transferring them to another machine, as well as subsequent operations with it.
That is why such networks were suitable only for solving primitive problems. So, what is a local area network in the current sense? Modern office facilities must meet new requirements:
Sharing, protecting and transferring data;
Applications must be available for sharing;
Users should be comfortable interacting with each other;
Peripheral devices must be made available to all machines.
Now you know not only what a local area network is, but also what are the principles underlying it.
Today we will talk about how to install and configure a local server on your computer?!
This is necessary so that you can develop and debug your scripts in PHP, since PHP is a programming language designed to generate HTML pages that runs on a web server and works with databases.
Installing the Apache server and related programs manually can be quite a tedious task. The fact is that you will have to deal with numerous Apache, PHP and MySQL configuration options that you will never need again.
In order to simplify the entire installation process as much as possible, a complex was created " Gentleman's set of a web developer", which contains the same distributions of Apache, PHP, MySQL and Perl, combined into a single archive, equipped with a convenient installer and configuration utilities for a specific machine.
To download this set follow the link http://www.denwer.ru/. This is the official Denver developer site. Download from there latest version Denver.
After you have downloaded the distribution, you need to run it. First, the archive will be unpacked to a temporary directory, and then the installer will automatically start.
Next, you will be asked in which directory you would like to install the complex (the default is C:\webserver, you only need to press the "Enter" key to accept this choice). Absolutely all system components will be installed in the specified directory.

After that, copying of the distribution files will begin, and at the end you will be asked how exactly you are going to start and stop the complex. You have two options:
- Automatically create a virtual disk when the machine boots, and do not disconnect it (virtual disk) when the server is stopped. This is the most convenient mode. I recommend choosing it!
- Create a virtual disk, only manually, at the command to start the complex (by clicking on the launch shortcut on the desktop). And, accordingly, disconnect the disk from the system - when the server stops.

Well, that's all. Installation completed. Immediately click on the shortcut created by the installer "Startservers" on the desktop and then wait for all console windows to disappear.
In order to check the operation of the local server, open your browser and type in the address: http://localhost. If everything went well, you will see the following window:

So great! Now let's create a test site on the local server, which will have the address http://test.ru . To do this, open the directory where you installed the distribution (C:\WebServers by default). It contains 4 folders.
 So, remember, all your sites must be created in the folder "home"! To do this, open the "home" folder and create a directory in it with a name that matches the name of your future site (in our case, it will be a directory with the name test.ru
). Now in the "test.ru" folder we will create another folder and name it " www
". It is in this folder that all the files of our site will be stored.
So, remember, all your sites must be created in the folder "home"! To do this, open the "home" folder and create a directory in it with a name that matches the name of your future site (in our case, it will be a directory with the name test.ru
). Now in the "test.ru" folder we will create another folder and name it " www
". It is in this folder that all the files of our site will be stored.
After all folders are created, you need to restart the server. To do this, use the label "Restart servers" on the desktop.
That's all there is to it. Now you can easily upload your files to the local server in the folder home/test.ru/www . And in order to check them, in your browser you need to type the address http://test.ru.
That's all! Good luck!